Revised recommendations of the Italian Society of Pediatrics about the general management of Kawasaki disease
- PMID: 33494789
- PMCID: PMC7830049
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-021-00962-4
Revised recommendations of the Italian Society of Pediatrics about the general management of Kawasaki disease
Abstract
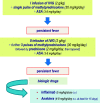
Aim of these revised recommendations for the general management of Kawasaki disease is to encourage its prompter recognition and warrant the most appropriate therapy, based on ascertained scientific data, raising awareness of the complications related to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment. A set of 20 synthetic operative statements is herein provided, including the definition of Kawasaki disease, its protean presentations, clinical course and seminal treatment modalities of all disease phases. The application of these recommendations should improve prognosis of Kawasaki disease and prevent the progression to permanent vascular abnormalities, thereby diminishing morbidity and mortality.
Keywords: Aspirin; Children; Coronary artery abnormalities; Intravenous immunoglobulin; Kawasaki disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Marchesi A, Tarissi De Jacobis I, Rigante D, Rimini A, Malorni W, Corsello G, et al. Kawasaki disease: guidelines of the Italian Society of Pediatrics, part I - definition, epidemiology, etiopathogenesis, clinical expression and management of the acute phase. Ital J Pediatr. 2018;44:102. doi: 10.1186/s13052-018-0536-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marchesi A, Tarissi De Jacobis I, Rigante D, Rimini A, Malorni W, Corsello G, et al. Kawasaki disease: guidelines of Italian Society of Pediatrics, part II - treatment of resistant forms and cardiovascular complications, follow-up, lifestyle and prevention of cardiovascular risks. Ital J Pediatr. 2018;44:103. doi: 10.1186/s13052-018-0529-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kawasaki T. Acute febrile mucocutaneus syndrome with lymphoid involvement with specific desquamation of the finger and toes in children. Arerugi. 1967;16:178–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

