AbaM Regulates Quorum Sensing, Biofilm Formation, and Virulence in Acinetobacter baumannii
- PMID: 33495249
- PMCID: PMC8088503
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00635-20
AbaM Regulates Quorum Sensing, Biofilm Formation, and Virulence in Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
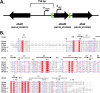
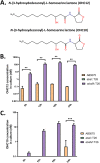
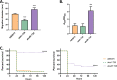
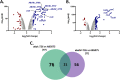
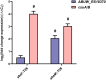
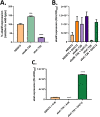
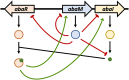
Acinetobacter baumannii possesses a single divergent luxR/luxRI-type quorum-sensing (QS) locus named abaR/abaI This locus also contains a third gene located between abaR and abaI, which we term abaM, that codes for an uncharacterized member of the RsaM protein family known to regulate N-acylhomoserine lactone (AHL)-dependent QS in other beta- and gammaproteobacteria. Here, we show that disruption of abaM via a T26 insertion in A. baumannii strain AB5075 resulted in increased production of N-(3-hydroxydodecanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone and enhanced surface motility and biofilm formation. In contrast to the wild type and the abaI::T26 mutant, the virulence of the abaM::T26 mutant was completely attenuated in a Galleria mellonella infection model. Transcriptomic analysis of the abaM::T26 mutant revealed that AbaM differentially regulates at least 76 genes, including the csu pilus operon and the acinetin 505 lipopeptide biosynthetic operon, that are involved in surface adherence, biofilm formation and virulence. A comparison of the wild type, abaM::T26 and abaI::T26 transcriptomes, indicates that AbaM regulates ∼21% of the QS regulon including the csu operon. Moreover, the QS genes (abaI and abaR) were among the most upregulated in the abaM::T26 mutant. A. baumanniilux-based abaM reporter gene fusions revealed that abaM expression is positively regulated by QS but negatively autoregulated. Overall, the data presented in this work demonstrates that AbaM plays a central role in regulating A. baumannii QS, virulence, surface motility, and biofilm formation.IMPORTANCEAcinetobacter baumannii is a multiantibiotic-resistant pathogen of global health care importance. Understanding Acinetobacter virulence gene regulation could aid the development of novel anti-infective strategies. In A. baumannii, the abaR and abaI genes that code for the receptor and synthase components of an N-acylhomoserine (AHL) lactone-dependent quorum sensing system (QS) are separated by abaM Here, we show that although mutation of abaM increased AHL production, surface motility, and biofilm development, it resulted in the attenuation of virulence. AbaM was found to control both QS-dependent and QS-independent genes. The significance of this work lies in the identification of AbaM, an RsaM ortholog known to control virulence in plant pathogens, as a modulator of virulence in a human pathogen.
Keywords: Acinetobacter; N-acylhomoserine lactones; RsaM; biofilm; quorum sensing; virulence.
Copyright © 2021 López-Martín et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of AbaI mutation on virulence, biofilm development, and antibiotic susceptibility in Acinetobacter baumannii.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 14;14(1):21521. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72740-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39277662 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of the AbaI/AbaR Quorum Sensing System to Resistance and Virulence of Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Strains.Infect Drug Resist. 2020 Nov 24;13:4273-4281. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S276970. eCollection 2020. Infect Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 33262621 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Inhibitory Effect of Polymyxin B in Combination with Ceftazidime against Robust Biofilm Formed by Acinetobacter baumannii with Genetic Deficiency in AbaI/AbaR Quorum Sensing.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0176821. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01768-21. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35196792 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum sensing in Acinetobacter: an emerging pathogen.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2010 Nov;36(4):349-60. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2010.512269. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20846031 Review.
-
Quorum-sensing system in Acinetobacter baumannii: a potential target for new drug development.J Appl Microbiol. 2020 Jan;128(1):15-27. doi: 10.1111/jam.14330. Epub 2019 Jun 26. J Appl Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31102552 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Pleural Fluid and Human Serum Albumin Modulate the Behavior of a Hypervirulent and Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) Acinetobacter baumannii Representative Strain.Pathogens. 2021 Apr 13;10(4):471. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10040471. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 33924559 Free PMC article.
-
Types and Mechanisms of Efflux Pump Systems and the Potential of Efflux Pump Inhibitors in the Restoration of Antimicrobial Susceptibility, with a Special Reference to Acinetobacter baumannii.Pathogens. 2024 Feb 23;13(3):197. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13030197. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38535540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Serum Albumin, a Component of Human Pleural Fluid, on Transcriptional and Phenotypic Changes on Acinetobacter baumannii A118.Curr Microbiol. 2021 Nov;78(11):3829-3834. doi: 10.1007/s00284-021-02649-9. Epub 2021 Sep 14. Curr Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34522980 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Acinetobacter baumannii with Human Serum Albumin: Does the Host Determine the Outcome?Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Jul 8;10(7):833. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10070833. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356754 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic AMP is a global virulence regulator governing inter and intrabacterial signalling in Acinetobacter baumannii.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Sep 6;20(9):e1012529. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012529. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39241032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. 2017. WHO publishes list of bacteria for which new antibiotics are urgently needed. Saudi Med J 38:444–445.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

