Plitidepsin has potent preclinical efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 by targeting the host protein eEF1A
- PMID: 33495306
- PMCID: PMC7963220
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abf4058
Plitidepsin has potent preclinical efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 by targeting the host protein eEF1A
Abstract
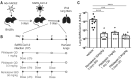
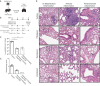
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) viral proteins interact with the eukaryotic translation machinery, and inhibitors of translation have potent antiviral effects. We found that the drug plitidepsin (aplidin), which has limited clinical approval, possesses antiviral activity (90% inhibitory concentration = 0.88 nM) that is more potent than remdesivir against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro by a factor of 27.5, with limited toxicity in cell culture. Through the use of a drug-resistant mutant, we show that the antiviral activity of plitidepsin against SARS-CoV-2 is mediated through inhibition of the known target eEF1A (eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1A). We demonstrate the in vivo efficacy of plitidepsin treatment in two mouse models of SARS-CoV-2 infection with a reduction of viral replication in the lungs by two orders of magnitude using prophylactic treatment. Our results indicate that plitidepsin is a promising therapeutic candidate for COVID-19.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures



Comment in
-
SARS-CoV-2 dependence on host pathways.Science. 2021 Feb 26;371(6532):884-885. doi: 10.1126/science.abg6837. Science. 2021. PMID: 33632832 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization, “Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV)”; www.who.int/emergencies/mers-cov/en/.
-
- Wang D., Hu B., Hu C., Zhu F., Liu X., Zhang J., Wang B., Xiang H., Cheng Z., Xiong Y., Zhao Y., Li Y., Wang X., Peng Z., Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 323, 1061–1069 (2020). 10.1001/jama.2020.1585 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN272201400008C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI120694/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI135990/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI122747/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA239333/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA221969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA244550/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK130425/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI135972/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI063302/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AI150476/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI143292/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI160706/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

