Radiotherapy Delivered before CDK4/6 Inhibitors Mediates Superior Therapeutic Effects in ER+ Breast Cancer
- PMID: 33495311
- PMCID: PMC8327758
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3871
Radiotherapy Delivered before CDK4/6 Inhibitors Mediates Superior Therapeutic Effects in ER+ Breast Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Recent preclinical data suggest that cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibition may be harnessed to sensitize estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer to radiotherapy. However, these findings were obtained in human ER+ breast cancer cell lines exposed to subclinical doses of CDK4/6 inhibitors with limited attention to treatment schedule. We investigated the activity of radiotherapy combined with the prototypic CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib placing emphasis on therapeutic schedule.
Experimental design: We combined radiotherapy and palbociclib in various doses and therapeutic schedules in human and mouse models of ER+ and ER-negative (ER-) breast cancer, including an immunocompetent mouse model that recapitulates key features of human luminal B breast cancer in women. We assessed proliferation, cell death, cell-cycle control, and clonogenic survival in vitro, as well as tumor growth, overall survival, and metastatic dissemination in vivo.
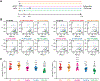
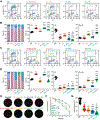
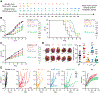
Results: Radiotherapy and palbociclib employed as standalone agents had partial cytostatic effects in vitro, correlating with suboptimal tumor control in vivo. However, while palbociclib delivered before focal radiotherapy provided minimal benefits as compared with either treatment alone, delivering focal radiotherapy before palbociclib mediated superior therapeutic effects, even in the absence of p53. Such superiority manifested in vitro with enhanced cytostasis and loss of clonogenic potential, as well as in vivo with improved local and systemic tumor control.
Conclusions: Our preclinical findings demonstrate that radiotherapy delivered before CDK4/6 inhibitors mediates superior antineoplastic effects compared with alternative treatment schedules, calling into question the design of clinical trials administering CDK4/6 inhibitors before radiotherapy in women with ER+ breast cancer.
©2021 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dual Targeting of CDK4/6 and BCL2 Pathways Augments Tumor Response in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Aug 1;26(15):4120-4134. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1872. Epub 2020 Apr 3. Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32245900
-
Palbociclib:CDK4/6 inhibition in the treatment of ER-positive breast cancer.Drugs Today (Barc). 2016 Feb;52(2):119-29. doi: 10.1358/dot.2016.52.2.2440528. Drugs Today (Barc). 2016. PMID: 27092341 Review.
-
Serum thymidine kinase 1 activity as a pharmacodynamic marker of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibition in patients with early-stage breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant palbociclib.Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Nov 21;19(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s13058-017-0913-7. Breast Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29162134 Free PMC article.
-
Palbociclib and beyond for the treatment of HR + HER2- metastatic breast cancer: an Asian-Pacific perspective and practical management guide on the use of CDK4/6 inhibitors.Curr Med Res Opin. 2020 Aug;36(8):1363-1373. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2020.1783646. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Curr Med Res Opin. 2020. PMID: 32544344
-
Mechanisms of therapeutic CDK4/6 inhibition in breast cancer.Semin Oncol. 2017 Dec;44(6):385-394. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2018.01.006. Semin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29935900 Review.
Cited by
-
Perspectives in immunotherapy: meeting report from the immunotherapy bridge (December 2nd-3rd, 2020, Italy).J Transl Med. 2021 Jun 2;19(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02895-2. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34078406 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor inhibition mediates radiosensitization of ER-positive breast cancer models.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2022 Mar 10;8(1):31. doi: 10.1038/s41523-022-00397-y. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35273179 Free PMC article.
-
A new perspective on the proper timing of radiotherapy during CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy in patients with "bone-only" metastatic breast cancer.Pathol Oncol Res. 2023 Oct 11;29:1611369. doi: 10.3389/pore.2023.1611369. eCollection 2023. Pathol Oncol Res. 2023. PMID: 37886029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CYPD limits HR+ mammary carcinogenesis in mice.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Jun 10;11(1):273. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02555-0. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40494873 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation therapy: An old dog learning new tricks.Methods Cell Biol. 2022;172:xiii-xxiii. doi: 10.1016/S0091-679X(22)00139-X. Methods Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 36064230 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 2019;69: 7–34. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Neven P, Chia S, Fasching PA, De Laurentiis M, Im SA, et al. Overall survival with ribociclib plus fulvestrant in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2020;382:514–24. - PubMed
-
- O’Leary B, Finn RS, Turner NC. Treating cancer with selective CDK4/6 inhibitors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2016;13:417–30. - PubMed
-
- Cox JA, Swanson TA. Current modalities of accelerated partial breast irradiation. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2013;10:344–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

