Drosophila Sex Peptide controls the assembly of lipid microcarriers in seminal fluid
- PMID: 33495334
- PMCID: PMC7865141
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2019622118
Drosophila Sex Peptide controls the assembly of lipid microcarriers in seminal fluid
Abstract
Seminal fluid plays an essential role in promoting male reproductive success and modulating female physiology and behavior. In the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, Sex Peptide (SP) is the best-characterized protein mediator of these effects. It is secreted from the paired male accessory glands (AGs), which, like the mammalian prostate and seminal vesicles, generate most of the seminal fluid contents. After mating, SP binds to spermatozoa and is retained in the female sperm storage organs. It is gradually released by proteolytic cleavage and induces several long-term postmating responses, including increased ovulation, elevated feeding, and reduced receptivity to remating, primarily signaling through the SP receptor (SPR). Here, we demonstrate a previously unsuspected SPR-independent function for SP. We show that, in the AG lumen, SP and secreted proteins with membrane-binding anchors are carried on abundant, large neutral lipid-containing microcarriers, also found in other SP-expressing Drosophila species. These microcarriers are transferred to females during mating where they rapidly disassemble. Remarkably, SP is a key microcarrier assembly and disassembly factor. Its absence leads to major changes in the seminal proteome transferred to females upon mating. Males expressing nonfunctional SP mutant proteins that affect SP's binding to and release from sperm in females also do not produce normal microcarriers, suggesting that this male-specific defect contributes to the resulting widespread abnormalities in ejaculate function. Our data therefore reveal a role for SP in formation of seminal macromolecular assemblies, which may explain the presence of SP in Drosophila species that lack the signaling functions seen in Dmelanogaster.
Keywords: Sex Peptide; reproduction; secretion; seminal proteins; triacylglycerides.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

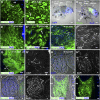
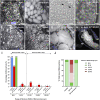



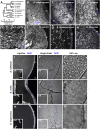
References
-
- Montagnon D., Valtat B., Vignon F., Koll-Back M. H., Secretory proteins of human seminal vesicles and their relationship to lipids and sugars. Andrologia 22 (suppl. 1), 193–205 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Veveris-Lowe T. L., Kruger S. J., Walsh T., Gardiner R. A., Clements J. A., Seminal fluid characterization for male fertility and prostate cancer: Kallikrein-related serine proteases and whole proteome approaches. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 33, 87–99 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Pampalakis G., Sotiropoulou G., Tissue kallikrein proteolytic cascade pathways in normal physiology and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1776, 22–31 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 107457/Z/15/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 097813/11/Z /WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/L007096/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/N016300/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 102347/Z/13/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/R004862/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/K014544/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- C19591/A19076/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 19076/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R35 GM122592/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 091911/B/10/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/K017462/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 091911/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 107457/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- C602/A18974/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- BB/T008881/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- C38302/A12278/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

