Structural insights into the disruption of TNF-TNFR1 signalling by small molecules stabilising a distorted TNF
- PMID: 33495441
- PMCID: PMC7835368
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-20828-3
Structural insights into the disruption of TNF-TNFR1 signalling by small molecules stabilising a distorted TNF
Abstract
Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) is a trimeric protein which signals through two membrane receptors, TNFR1 and TNFR2. Previously, we identified small molecules that inhibit human TNF by stabilising a distorted trimer and reduce the number of receptors bound to TNF from three to two. Here we present a biochemical and structural characterisation of the small molecule-stabilised TNF-TNFR1 complex, providing insights into how a distorted TNF trimer can alter signalling function. We demonstrate that the inhibitors reduce the binding affinity of TNF to the third TNFR1 molecule. In support of this, we show by X-ray crystallography that the inhibitor-bound, distorted, TNF trimer forms a complex with a dimer of TNFR1 molecules. This observation, along with data from a solution-based network assembly assay, leads us to suggest a model for TNF signalling based on TNF-TNFR1 clusters, which are disrupted by small molecule inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
D.Mc., C.M., J.P., D.F., R.G., P.M., T.C., B.C., A.L., T.B. and J.O’C are/were all employees of UCB Pharma and may hold stock and/or stock options.
Figures

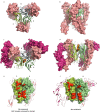
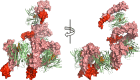


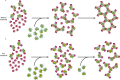

References
-
- Grell M, Scheurich P, Meager A, Pfizenmaier K. TR60 and TR80 tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-receptors can independently mediate cytosis. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1993;12:143–148. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

