Deletion of TLR4 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis
- PMID: 33495514
- PMCID: PMC8463538
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-020-00597-x
Deletion of TLR4 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis
Abstract
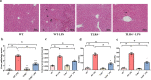
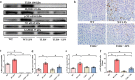
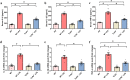
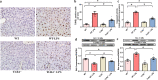
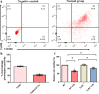
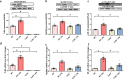
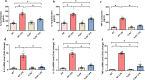
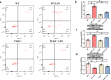
Septic acute liver injury is one of the leading causes of fatalities in patients with sepsis. Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) plays a vital role in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge, but the mechanisms underlying TLR4 function in septic injury remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the role of TLR4 in LPS-induced acute liver injury (ALI) in mice with a focus on inflammation and apoptosis. Wild-type (WT) and TLR4-knockout (TLR4-/-) mice were challenged with LPS (4 mg/kg) for 6 h. TLR4 signaling cascade markers (TLR4, MyD88, and NF-κB), inflammatory markers (TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6), and apoptotic markers (Bax, Bcl-2, and caspase 3) were evaluated. We showed that LPS challenge markedly increased the levels of serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT)/aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and other liver pathological changes in WT mice. In addition, LPS challenge elevated the levels of liver carbonyl proteins and serum inflammatory cytokines, upregulated the expression of TLR4, MyD88, and phosphorylated NF-κB in liver tissues. Moreover, LPS challenge significantly increased hepatocyte apoptosis, caspase 3 activity, and Bax level while suppressing Bcl-2 expression in liver tissues. These pathological changes were greatly attenuated in TLR4-/- mice. Similar pathological responses were provoked in primary hepatic Kupffer cells isolated from WT and TLR4-/- mice following LPS (1 μg/mL, 6 h) challenge. In summary, these results demonstrate that silencing of TLR4 attenuates LPS-induced liver injury through inhibition of inflammation and apoptosis via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. TLR4 deletion confers hepatoprotection against ALI induced by LPS, possibly by repressing macrophage inflammation and apoptosis.
Keywords: LPS; TLR4; TLR4−/− mice; acute liver injury; apoptosis; inflammation; primary hepatic Kupffer cells; sepsis.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to CPS and SIMM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatocyte-Conditional Knockout of Phosphatidylethanolamine Binding Protein 4 Aggravated LPS/D-GalN-Induced Acute Liver Injury via the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 8;13:901566. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.901566. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35874667 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol attenuates inflammatory response and apoptosis to protect d-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide induced acute liver injury via regulating TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Dec;77:105974. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105974. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31735662
-
β-arrestin 2 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury via inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway-mediated inflammation in mice.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jan 14;24(2):216-225. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i2.216. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29375207 Free PMC article.
-
IRF3 function and immunological gaps in sepsis.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 5;15:1336813. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1336813. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38375470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective effects of 17-β-estradiol on liver injury: The role of TLR4 signaling pathway and inflammatory response.Cytokine. 2024 Sep;181:156686. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2024.156686. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Cytokine. 2024. PMID: 38991382 Review.
Cited by
-
Lobetyolin protects mice against LPS-induced sepsis by downregulating the production of inflammatory cytokines in macrophage.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 10;15:1405163. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1405163. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38799158 Free PMC article.
-
The Contribution of Hepatic Macrophage Heterogeneity during Liver Regeneration after Partial Hepatectomy in Mice.J Immunol Res. 2022 Oct 7;2022:3353250. doi: 10.1155/2022/3353250. eCollection 2022. J Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 36249420 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory effects of mangiferin on LPS-induced inflammatory responses and intestinal flora imbalance during sepsis.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Dec 27;12(3):2068-2080. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3907. eCollection 2024 Mar. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38455195 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-206-3p alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting inflammation and pyroptosis through modulating TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway.Sci Rep. 2024 May 24;14(1):11860. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62733-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38789583 Free PMC article.
-
Chlojaponilactone B Attenuates THP-1 Macrophage Pyroptosis by Inhibiting the TLR/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Mar 21;17(3):402. doi: 10.3390/ph17030402. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guo FM, Qiu HB. Definition and dignosis of sepsis 3.0. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2016;55:420–32. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

