Anopheles stephensi Mosquitoes as Vectors of Plasmodium vivax and falciparum, Horn of Africa, 2019
- PMID: 33496217
- PMCID: PMC7853561
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2702.200019
Anopheles stephensi Mosquitoes as Vectors of Plasmodium vivax and falciparum, Horn of Africa, 2019
Abstract
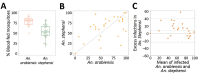
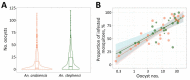
Anopheles stephensi mosquitoes, efficient vectors in parts of Asia and Africa, were found in 75.3% of water sources surveyed and contributed to 80.9% of wild-caught Anopheles mosquitoes in Awash Sebat Kilo, Ethiopia. High susceptibility of these mosquitoes to Plasmodium falciparum and vivax infection presents a challenge for malaria control in the Horn of Africa.
Keywords: Anopheles stephensi; Horn of Africa; Plasmodium falciparum; Plasmodium vivax; emerging; membrane feeding; mosquitoes; outbreak; parasites; transmission; urban malaria; vector competence.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Vector alert: Anopheles stephensi invasion and spread [cited 2020 Sep 3]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/vector-alert-anopheles-stephensi...
-
- World Health Organization. Larval source management: a supplementary measure for malaria vector control: an operational manual [cited 2020 Dec 21]. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/85379/9789241505604_eng...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

