Vocal development in a large-scale crosslinguistic corpus
- PMID: 33497512
- PMCID: PMC8310893
- DOI: 10.1111/desc.13090
Vocal development in a large-scale crosslinguistic corpus
Abstract
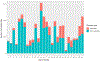
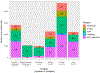
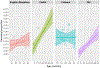
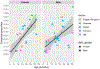
This study evaluates whether early vocalizations develop in similar ways in children across diverse cultural contexts. We analyze data from daylong audio recordings of 49 children (1-36 months) from five different language/cultural backgrounds. Citizen scientists annotated these recordings to determine if child vocalizations contained canonical transitions or not (e.g., "ba" vs. "ee"). Results revealed that the proportion of clips reported to contain canonical transitions increased with age. Furthermore, this proportion exceeded 0.15 by around 7 months, replicating and extending previous findings on canonical vocalization development but using data from the natural environments of a culturally and linguistically diverse sample. This work explores how crowdsourcing can be used to annotate corpora, helping establish developmental milestones relevant to multiple languages and cultures. Lower inter-annotator reliability on the crowdsourcing platform, relative to more traditional in-lab expert annotators, means that a larger number of unique annotators and/or annotations are required, and that crowdsourcing may not be a suitable method for more fine-grained annotation decisions. Audio clips used for this project are compiled into a large-scale infant vocalization corpus that is available for other researchers to use in future work.
Keywords: babbling; crosslinguistic; crowdsourcing; infants; naturalistic recording; speech; vocal development.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


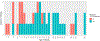
References
-
- Adolph KE, Karasik LB, & Tamis-LeMonda CS (2009). Motor skills. In Bornstein M (Ed.), Handbook of cultural developmental science (pp. 61–88). Taylor & Francis.
-
- Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, & Walker S (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67(1), 1–48.
-
- Belardi K, Watson LR, Faldowski RA, Hazlett H, Crais E, Baranek GT, Oller DK (2017). A retrospective video analysis of canonical babbling and volubility in infants with Fragile X syndrome at 9–12 months of age. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 47(4), 1193–1206. 10.1007/s10803-017-3033-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

