Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva
- PMID: 33497538
- PMCID: PMC7888461
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.13737
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva
Abstract
In the fight against the recent COVID-19 pandemics, testing is crucial. Nasopharyngeal swabs and real-time RT-PCR are used for the detection of the viral RNA. The collection of saliva is non-invasive, pain-free and does not require trained personnel. An alternative to RT-PCR is loop-mediated isothermal amplification coupled with reverse transcription (RT-LAMP) that is easy to perform, quick and does not require a thermal cycler. The aim of this study was to test whether SARS-CoV-2 RNA can be detected directly in saliva using RT-LAMP. We have tested 16 primer mixes from the available literature in three rounds of sensitivity assays. The selected RT-LAMP primer mix has a limit of detection of 6 copies of viral RNA per reaction in comparison with RT-PCR with 1 copy per reaction. Whole saliva, as well as saliva collected using Salivette collection tubes, interfered with the RT-LAMP analysis. Neither Chelex-100 nor protease treatment of saliva prevented the inhibitory effect of saliva. With the addition of the ribonuclease inhibitor, the sensitivity of the RT-LAMP assay was 12 copies per reaction of RNA in Salivette® saliva samples and 6 copies per reaction of RNA in whole saliva samples. This study shows that it is possible to combine the use of saliva and RT-LAMP for SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection without RNA extraction which was confirmed on a small set of correctly diagnosed clinical samples. Further studies should prove whether this protocol is suitable for point of care testing in the clinical setting.
© 2021 The Authors. Microbial Biotechnology published by Society for Applied Microbiology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

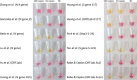





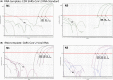
References
-
- Ceder, O. , van Dijken, J. , Ericson, T. , and Kollberg, H. (1985) Ribonuclease in different types of saliva from cystic fibrosis patients. Acta Paediatr Scand 74: 102–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

