Schwann cell remyelination of the central nervous system: why does it happen and what are the benefits?
- PMID: 33497588
- PMCID: PMC7881176
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.200352
Schwann cell remyelination of the central nervous system: why does it happen and what are the benefits?
Abstract
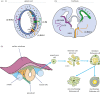
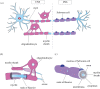
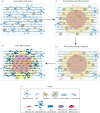
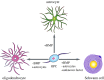
Myelin sheaths, by supporting axonal integrity and allowing rapid saltatory impulse conduction, are of fundamental importance for neuronal function. In response to demyelinating injuries in the central nervous system (CNS), oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs) migrate to the lesion area, proliferate and differentiate into new oligodendrocytes that make new myelin sheaths. This process is termed remyelination. Under specific conditions, demyelinated axons in the CNS can also be remyelinated by Schwann cells (SCs), the myelinating cell of the peripheral nervous system. OPCs can be a major source of these CNS-resident SCs-a surprising finding given the distinct embryonic origins, and physiological compartmentalization of the peripheral and central nervous system. Although the mechanisms and cues governing OPC-to-SC differentiation remain largely undiscovered, it might nevertheless be an attractive target for promoting endogenous remyelination. This article will (i) review current knowledge on the origins of SCs in the CNS, with a particular focus on OPC to SC differentiation, (ii) discuss the necessary criteria for SC myelination in the CNS and (iii) highlight the potential of using SCs for myelin regeneration in the CNS.
Keywords: Schwann cells; astrocytes; central nervous system; myelin; oligodendrocyte progenitor cells; remyelination.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Blakemore WF 1976. Invasion of Schwann cells into the spinal cord of the rat following local injections of lysolecithin. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2, 21–39. (10.1111/j.1365-2990.1976.tb00559.x) - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
