Emotional processes in binge drinking: A systematic review and perspective
- PMID: 33497920
- PMCID: PMC8275688
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cpr.2021.101971
Emotional processes in binge drinking: A systematic review and perspective
Abstract
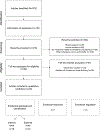
Binge drinking is a widespread alcohol consumption pattern commonly engaged by youth. Here, we present the first systematic review of emotional processes in relation to binge drinking. Capitalizing on a theoretical model describing three emotional processing steps (emotional appraisal/identification, emotional response, emotional regulation) and following PRISMA guidelines, we considered all identified human studies exploring emotional abilities among binge drinkers. A literature search was conducted in PubMed, Scopus, and PsychINFO, and a standardized methodological quality assessment was performed for each study. The main findings offered by the 43 studies included are: 1) regarding emotional appraisal/identification, binge drinking is related to heightened negative emotional states, including greater severity of depressive and anxiety symptoms, and have difficulties in recognizing emotional cues expressed by others; 2) regarding emotional response, binge drinkers exhibit diminished emotional response compared with non-binge drinkers; 3) regarding emotional regulation, no experimental data currently support impaired emotion regulation in binge drinking. Variability in the identification and measurement of binge drinking habits across studies limits conclusions. Nevertheless, current findings establish the relevance of emotional processes in binge drinking and set the stage for new research perspectives to identify the nature and extent of emotional impairments in the onset and maintenance of excessive alcohol use.
Keywords: Alcohol; Binge drinking; Emotional identification; Emotional response.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
None.
Figures

References
-
- Alaux-Cantin S, Warnault V, Legastelois R, Botia B, Pierrefiche O, Vilpoux C, & Naassila M (2013). Alcohol intoxications during adolescence increase motivation for alcohol in adult rats and induce neuroadaptations in the nucleus accumbens. Neuropharmacology, 67, 521–531. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.12.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Black MH, Chen NTM, Iyer KK, Lipp OV, Bölte S, Falkmer M, … Girdler S (2017). Mechanisms of facial emotion recognition in autism spectrum disorders: Insights from eye tracking and electroencephalography. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 80, 488–515. 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.06.016 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

