The COVID-19 pandemic face mask waste: A blooming threat to the marine environment
- PMID: 33497928
- PMCID: PMC7836388
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129601
The COVID-19 pandemic face mask waste: A blooming threat to the marine environment
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "The COVID-19 pandemic face mask waste: A blooming threat to the marine environment" [Chemosphere 272 (2021) 129601].Chemosphere. 2022 Jan;287(Pt 4):132411. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132411. Epub 2021 Oct 2. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 34610540 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
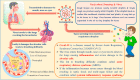
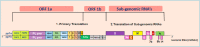
Recently, the COVID-19 disease spread has emerged as a worldwide pandemic and cause severe threats to humanity. The World Health Organisation (WHO) releases guidelines to help the countries to reduce the spread of this virus to the public, like wearing masks, hand hygiene, social distancing, shutting down all types of public transports, etc. These conditions led to a worldwide economic fall drastically, and on the other hand, indirect environmental benefits like global air quality improvement and decreased water pollution are also pictured. Currently, use of face masks is part of a comprehensive package of the prevention and control measures that can limit the spread of COVID-19 since there is no clinically proven drugs or vaccine available for COVID-19. Mostly, face masks are made of petroleum-based non-renewable polymers that are non-biodegradable, hazardous to the environment and create health issues. This study demonstrates the extensive use of the face mask and how it affects human health and the marine ecosystem. It has become a great challenge for the government sectors to impose strict regulations for the proper disposal of the masks as medical waste by the public. Neglecting the seriousness of this issue may lead to the release of large tonnes of micro-plastics to the landfill as well as to the marine environment where mostly end-up and thereby affecting their fauna and flora population vastly. Besides, this study highlights the COVID-19 spread, its evolutionary importance, taxonomy, genomic structure, transmission to humans, prevention, and treatment.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Face mask; Marine environment; Pollution.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Abbasinia M., Karimie S., Haghighat M., Mohammadfam I. Application of nanomaterials in personal respiratory protection equipment: a literature review. Saf. Now. 2018;4:47.
-
- Adams M.J., Lefkowitz E.J., King A.M.Q., Harrach B., Harrison R.L., Knowles N.J., Kropinski A.M., Krupovic M., Kuhn J.H., Mushegian A.R., Nibert M.L., Sabanadzovic S., Sanfaçon H., Siddell S.G., Simmonds P., Varsani A., Zerbini F.M., Orton R.J., Smith D.B., Gorbalenya A.E., Davison A.J. 50 years of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses: progress and prospects. Arch. Virol. 2017;162:1441–1446. - PubMed
-
- Adhikari S.P., Meng S., Wu Y.J., Mao Y.P., Ye R.X., Wang Q.Z., Sun C., Sylvia S., Rozelle S., Raat H., Zhou H. Epidemiology, causes, clinical manifestation and diagnosis, prevention and control of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) during the early outbreak period: a scoping review. Infect. Dis Poverty. 2020;9:29. - PMC - PubMed
-
- AENOR UNE-EN 149:2001+A1:2010. Respiratory Protective Devices. Filtering half mask to protect against particles. 2010. https://www.aenor.com/normas-y-libros/buscador-de-normas/UNE?c=N0044643 Requirements, testing, marking. Available on 9th April 2020 at.
-
- AFNOR . Association française de Normalisation AFNOR; 2020. AFNOR SPEC S76-001 Barrier Masks. Guide to Minimum Requirements, Test Methods, Preparation and Use for Mass Manufactured and Homemade Masks.https://iv.revistalocal.es/wp-content/uploads/AFNORSpec-S76-001-Mascaril... Available on 9th of April 2020 at.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

