Evaluation of the geroprotective effects of withaferin A in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 33498013
- PMCID: PMC7880378
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.202572
Evaluation of the geroprotective effects of withaferin A in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
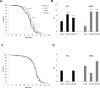
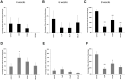
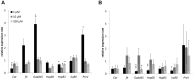
Withanolides are a class of compounds usually found in plant extracts which are an attractive geroprotective drug design starting point. We evaluated the geroprotective properties of Withaferin A (WA) in vivo using the Drosophila model. Flies were supplemented by nutrient medium with WA (at a concentration of 1, 10, or 100 μM dissolved in ethanol) for the experiment group and 30 μM of ethanol for the control group. WA treatment at 10 and 100 μM concentrations prolong the median life span of D. melanogaster's male by 7.7, 9.6% (respectively) and the maximum life span (the age of death 90% of individuals) by 11.1% both. Also WA treatment at 1, 10 and 100 μM improved the intestinal barrier permeability in older flies and affected an expression of genes involved in antioxidant defense (PrxV), recognition of DNA damage (Gadd45), heat shock proteins (Hsp68, Hsp83), and repair of double-strand breaks (Ku80). WA was also shown to have a multidirectional effect on the resistance of flies to the prooxidant paraquat (oxidative stress) and 33° C hyperthermia (heat shock). WA treatment increased the resistance to oxidative stress in males at 4 and 7 week old and decreased it at 6 weeks old. It increased the male's resistance to hyperthermia at 2, 4 and 7 weeks old and decreased it at 3, 5 and 8 weeks old. WA treatment decreased the resistance to hyperthermia in females at 1, 2 and 3 weeks old and not affected on their resistance to oxidative stress.
Keywords: Drosophila melanogaster; lifespan; stress response; stress-resistance; withaferin A.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Curcumin supplementation increases survival and lifespan in Drosophila under heat stress conditions.Biofactors. 2018 Nov;44(6):577-587. doi: 10.1002/biof.1454. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Biofactors. 2018. PMID: 30488487
-
Extension of Drosophila lifespan by Rosa damascena associated with an increased sensitivity to heat.Biogerontology. 2012 Apr;13(2):105-17. doi: 10.1007/s10522-011-9357-0. Epub 2011 Sep 18. Biogerontology. 2012. PMID: 21928072 Free PMC article.
-
[The protein oxidative damage level and lifespan modulation by xenobiotics in Drosophila melanogaster].Adv Gerontol. 2008;21(2):212-7. Adv Gerontol. 2008. PMID: 18942363 Russian.
-
Doxycycline-regulated over-expression of hsp22 has negative effects on stress resistance and life span in adult Drosophila melanogaster.Mech Ageing Dev. 2004 Sep;125(9):651-63. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2004.08.010. Mech Ageing Dev. 2004. PMID: 15491684
-
[The Antioxidant and Geroprotective Properties of an Extract of Mountain Ash (Sorbus aucuparia L.) Fruits].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2023 Nov-Dec;57(6):979-994. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2023. PMID: 38062954 Russian.
Cited by
-
Aging-associated Alterations in the Gene Regulatory Network Landscape Associate with Risk, Prognosis and Response to Therapy in Lung Adenocarcinoma.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 3:2024.07.02.601689. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.02.601689. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: NPJ Aging. 2025 Jul 9;11(1):61. doi: 10.1038/s41514-025-00247-8. PMID: 39005266 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Pterocarpus marsupium extract extends replicative lifespan in budding yeast.Geroscience. 2021 Oct;43(5):2595-2609. doi: 10.1007/s11357-021-00418-x. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Geroscience. 2021. PMID: 34297314 Free PMC article.
-
Chaperone Activators.Subcell Biochem. 2024;107:43-62. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-66768-8_3. Subcell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39693019 Review.
-
Aging-associated alterations in gene regulatory networks associate with risk, prognosis and response to therapy in lung adenocarcinoma.NPJ Aging. 2025 Jul 9;11(1):61. doi: 10.1038/s41514-025-00247-8. NPJ Aging. 2025. PMID: 40634311 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Longevity Potential of Natural Phytochemicals: A Comprehensive Review of Active Ingredients in Dietary Plants and Herbs.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Nov 13;72(45):24908-24927. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c07756. Epub 2024 Oct 31. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 39480905 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee SH, Min KJ. Drosophila melanogaster as a model system in the study of pharmacological interventions in aging. Transl Med Aging. 2019; 3:98–103.
-
- Yarden A, Lavie D. Constituents of Withania somnifera. Part I. The functional groups of withaferin. J Chem Soc. 1962; 2925–7. 10.1039/jr9620002925 - DOI
-
- Lavie D, Glotter E, Shvo Y. Constituents of Withania somnifera Dun. III. The side chain of withaferin A. J Org Chem. 1965; 30:1774–8. 10.1021/jo01017a015 - DOI
-
- Lavie D, Glotter E, Shvo Y. Constituents of Withania somnifera Dun. Part IV. The structure of withaferin A. J Chem Soc. 1965; 7517–31. 10.1039/jr9650007517 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

