Carbon Fiber-Silica Aerogel Composite with Enhanced Structural and Mechanical Properties Based on Water Glass and Ambient Pressure Drying
- PMID: 33498246
- PMCID: PMC7909270
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11020258
Carbon Fiber-Silica Aerogel Composite with Enhanced Structural and Mechanical Properties Based on Water Glass and Ambient Pressure Drying
Abstract
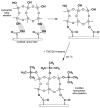
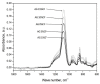
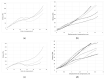
The article presents the synthesis of silica aerogel from a much cheaper precursor of water glass that was reinforced with short pitch carbon fiber by way of ambient pressure drying. Before being added to the silica gel, the carbon fibers were surface modified to increase adhesion at the interfacial border. We were able to obtain stable structures of the composite with the amount of fibers above 10% by volume. The presence of fibers in the silica matrix resulted in lower synthesis time of the composite, improved adhesion of fibers to the aerogel nanostructure, and increased mechanical and structural parameters. An additional effect of the presence of fibers in excess of 10% by volume was a new function of the nanocomposite-the ability to conduct electric current. The most optimal parameters of the composite, however, were obtained for silica aerogel reinforced with 10 vol.% of carbon fibers. This material indicated relatively low density and good physical parameters. The paper also analyzes the results on the synthesis of fiber-reinforced silica aerogels that have appeared in recent years and compares these to the results gained in presented work.
Keywords: ambient pressure drying APD; carbon microfibers: structural and mechanical properties; silica aerogel; water glass.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Investigation of mechanical and thermal behavior of fiber-reinforced silica xerogel composites.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 12;19(6):e0303293. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303293. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38865365 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Research on the Synthetic Fiber Based Silica Aerogel Nanocomposites.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017 Feb 16;7(2):44. doi: 10.3390/nano7020044. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28336876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbon Fiber and Nickel Coated Carbon Fiber-Silica Aerogel Nanocomposite as Low-Frequency Microwave Absorbing Materials.Materials (Basel). 2020 Jan 15;13(2):400. doi: 10.3390/ma13020400. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31952264 Free PMC article.
-
Polypropylene/Silica Aerogel Composite Incorporating a Conformal Coating of Methyltrimethoxysilane-Based Aerogel.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2019 Mar 1;19(3):1376-1381. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2019.16257. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30469191
-
Advances in precursor system for silica-based aerogel production toward improved mechanical properties, customized morphology, and multifunctionality: A review.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2020 Feb;276:102101. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2020.102101. Epub 2020 Jan 11. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2020. PMID: 31978639 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of mechanical and thermal behavior of fiber-reinforced silica xerogel composites.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 12;19(6):e0303293. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303293. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38865365 Free PMC article.
-
Spherical Attapulgite/Silica Aerogels Fabricated via Different Drying Methods with Excellent Adsorption Performance.Materials (Basel). 2023 Mar 13;16(6):2292. doi: 10.3390/ma16062292. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36984172 Free PMC article.
-
Robust Silica-Agarose Composite Aerogels with Interpenetrating Network Structure by In Situ Sol-Gel Process.Gels. 2022 May 16;8(5):303. doi: 10.3390/gels8050303. Gels. 2022. PMID: 35621601 Free PMC article.
-
Insulating materials based on silica aerogel composites: synthesis, properties and application.RSC Adv. 2024 Oct 29;14(47):34690-34707. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04976d. eCollection 2024 Oct 29. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39479483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improvement of the Mechanical Properties of Silica Aerogels for Thermal Insulation Applications through a Combination of Aramid Nanofibres and Microfibres.Gels. 2023 Jun 30;9(7):535. doi: 10.3390/gels9070535. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37504414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carlson G., Lewis D., McKinley K., Richardson J., Tillotson T. Aerogel commercialization: Technology, markets and costs. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 1995;186:372–379. doi: 10.1016/0022-3093(95)00069-0. - DOI
-
- Koebel M., Rigacci A., Achard P. Aerogel-based thermal superinsulation: An overview. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2012;63:315–339. doi: 10.1007/s10971-012-2792-9. - DOI
-
- Patel R.P., Purohit N.S., Suthar A.M. An overview of silica aerogels. Int. J. Chemtech Res. 2009;1:1052–1057.
-
- Suh D.J. Catalytic applications of composite aerogels. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 2004;350:314–319. doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2004.08.230. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

