Fate of Biodegradable Engineered Nanoparticles Used in Veterinary Medicine as Delivery Systems from a One Health Perspective
- PMID: 33498295
- PMCID: PMC7863917
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26030523
Fate of Biodegradable Engineered Nanoparticles Used in Veterinary Medicine as Delivery Systems from a One Health Perspective
Abstract
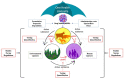
The field of veterinary medicine needs new solutions to address the current challenges of antibiotic resistance and the need for increased animal production. In response, a multitude of delivery systems have been developed in the last 20 years in the form of engineered nanoparticles (ENPs), a subclass of which are polymeric, biodegradable ENPs, that are biocompatible and biodegradable (pbENPs). These platforms have been developed to deliver cargo, such as antibiotics, vaccines, and hormones, and in general, have been shown to be beneficial in many regards, particularly when comparing the efficacy of the delivered drugs to that of the conventional drug applications. However, the fate of pbENPs developed for veterinary applications is poorly understood. pbENPs undergo biotransformation as they are transferred from one ecosystem to another, and these transformations greatly affect their impact on health and the environment. This review addresses nanoparticle fate and impact on animals, the environment, and humans from a One Health perspective.
Keywords: antibiotics; hormones; nanoparticles; one health; vaccines; veterinary medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Natural biodegradable polymers based nano-formulations for drug delivery: A review.Int J Pharm. 2019 Apr 20;561:244-264. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.03.011. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Int J Pharm. 2019. PMID: 30851391 Review.
-
Biodegradable Nanoparticles: A Recent Approach and Applications.Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21(16):1722-1732. doi: 10.2174/1389450121666200916091659. Curr Drug Targets. 2020. PMID: 32938346 Review.
-
Novel Biodegradable Polymer with Redox-Triggered Backbone Cleavage Through Sequential 1,6-Elimination and 1,5-Cyclization Reactions.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2017 Oct;38(19). doi: 10.1002/marc.201700395. Epub 2017 Aug 21. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2017. PMID: 28833950
-
Micromotors as "Motherships": A Concept for the Transport, Delivery, and Enzymatic Release of Molecular Cargo via Nanoparticles.Langmuir. 2019 Aug 13;35(32):10618-10624. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b01192. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Langmuir. 2019. PMID: 31322356
-
[Behaviors of engineered nanoparticles in aquatic environments and impacts on marine phytoplankton].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2015 Jan;36(1):365-72. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2015. PMID: 25898688 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Modulation of Bovine Endometrial Cell Receptors and Signaling Pathways as a Nanotherapeutic Exploration against Dairy Cow Postpartum Endometritis.Animals (Basel). 2021 May 23;11(6):1516. doi: 10.3390/ani11061516. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34071093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
One-Pot Surface Modification of β-Cu2O NPs for Biocatalytic Performance against A-549 Lung Carcinoma Cell Lines through Docking Analysis.ACS Omega. 2021 Oct 26;6(44):29380-29393. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c02942. eCollection 2021 Nov 9. ACS Omega. 2021. Retraction in: ACS Omega. 2023 Jun 22;8(26):24127. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c04284. PMID: 34778611 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Nanodelivery of essential oils as efficient tools against antimicrobial resistance: a review of the type and physical-chemical properties of the delivery systems and applications.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):1007-1024. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2056663. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35363104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current status of nano-vaccinology in veterinary medicine science.Vet Med Sci. 2023 Sep;9(5):2294-2308. doi: 10.1002/vms3.1221. Epub 2023 Jul 24. Vet Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37487030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Old Antibiotics Can Learn New Ways: A Systematic Review of Florfenicol Use in Veterinary Medicine and Future Perspectives Using Nanotechnology.Animals (Basel). 2023 May 19;13(10):1695. doi: 10.3390/ani13101695. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37238125 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moreno-Vega A.I., Gómez-Quintero T., Nuñez-Anita R.E., Acosta-Torres L.S., Castaño V. Polymeric and ceramic nanoparticles in biomedical applications. J. Nanotechnol. 2012;2012:936041. doi: 10.1155/2012/936041. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources