The Influence of Social Support on the Relationship between Emotional Demands and Health of Hospital Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 33498995
- PMCID: PMC7912004
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare9020115
The Influence of Social Support on the Relationship between Emotional Demands and Health of Hospital Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
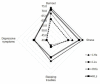
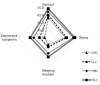
Social support reduces the negative results of emotional labor. A more detailed analysis should be performed to facilitate adequate social support for nurses. Therefore, this study was conducted to examine the relationships among nurses' emotional demands, social support, and health. A cross-sectional survey was conducted at two tertiary hospitals in South Korea. A sample of 117 nurses from eight units participated. Between-group differences in the main variables were analyzed using the t-test or Mann-Whitney test, and analysis of variance or the Kruskal-Wallis test. Nurses were classified into eight groups according to emotional demands and type of social support, and the effects of social support were analyzed based on mean scores. Greater social support from colleagues was associated with better health on all measures. However, greater social support from supervisors was associated with a higher incidence of burnout, stress, and sleeping troubles. Nurses' high emotional demands must be managed actively by hospitals to maintain and promote their health. Providing appropriate social support with consideration of the nurse's unit experience would help decrease the effects of emotional demands. Enhancing social support from nursing colleagues is a powerful way to manage the negative effects of nurses' emotional demands.
Keywords: burnout; emotional demands; nurse; social support; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Average hospital length of stay, nurses' work demands, and their health and job outcomes.J Nurs Scholarsh. 2014 May;46(3):199-206. doi: 10.1111/jnu.12066. Epub 2014 Feb 6. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2014. PMID: 24502556
-
Nurses' steps, distance traveled, and perceived physical demands in a three-shift schedule.Hum Resour Health. 2022 Oct 8;20(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12960-022-00768-3. Hum Resour Health. 2022. PMID: 36209110 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional Labor Strategies, Stress, and Burnout Among Hospital Nurses: A Path Analysis.J Nurs Scholarsh. 2020 Jan;52(1):105-112. doi: 10.1111/jnu.12532. Epub 2019 Nov 23. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2020. PMID: 31758662
-
Personal and work-related factors associated with nurse resilience: A systematic review.Int J Nurs Stud. 2019 May;93:129-140. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2019.02.014. Epub 2019 Mar 5. Int J Nurs Stud. 2019. PMID: 30925279
-
Emotional exhaustion and medication administration work-arounds: the moderating role of nurse satisfaction with medication administration.Health Care Manage Rev. 2013 Apr-Jun;38(2):95-104. doi: 10.1097/HMR.0b013e3182452c7f. Health Care Manage Rev. 2013. PMID: 22261669 Review.
Cited by
-
Impacts of Corporate Social Responsibility on Employees' Mental Fatigue: Employees' Ethical Perspective.Front Psychol. 2022 Jun 15;13:918106. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.918106. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35783729 Free PMC article.
-
Correlations between well-being of nurses and psychosocial working conditions - a descriptive cross-sectional study.Front Public Health. 2024 Jul 24;12:1443015. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1443015. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39114512 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring factors affecting nurse anxiety in Northwest Ethiopia: a multicenter study.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Oct 2;15:1434701. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1434701. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39415889 Free PMC article.
-
Differential impacts of internal and external corporate social responsibility on emotional labor among clinicians in Chinese public hospitals: A cross-sectional study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jul 25;104(30):e43276. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043276. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40725943 Free PMC article.
-
Work Environment Characteristics and Emotional Intelligence as Correlates of Nurses' Compassion Satisfaction and Compassion Fatigue: A Cross-Sectional Survey Study.Nurs Rep. 2021 Oct 26;11(4):847-858. doi: 10.3390/nursrep11040079. Nurs Rep. 2021. PMID: 34968273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schaufeli W.B., Bakker A.B., Van Rhenen W. How changes in job demands and resources predict burnout, work engagement, and sickness absenteeism. J. Organ. Behav. 2009;30:893–917. doi: 10.1002/job.595. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

