Advances in Nanocarriers for Effective Delivery of Docetaxel in the Treatment of Lung Cancer: An Overview
- PMID: 33499040
- PMCID: PMC7865793
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13030400
Advances in Nanocarriers for Effective Delivery of Docetaxel in the Treatment of Lung Cancer: An Overview
Abstract
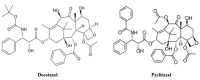
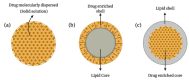
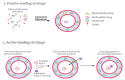
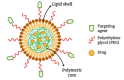
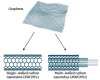
Docetaxel (DCX) is a highly effective chemotherapeutic drug used in the treatment of different types of cancer, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The drug is known to have low oral bioavailability due to its low aqueous solubility, poor membrane permeability and susceptibility to hepatic first-pass metabolism. To mitigate these problems, DCX is administered via the intravenous route. Currently, DCX is commercially available as a single vial that contains polysorbate 80 and ethanol to solubilize the poorly soluble drug. However, this formulation causes short- and long-term side effects, including hypersensitivity, febrile neutropenia, fatigue, fluid retention, and peripheral neuropathy. DCX is also a substrate to the drug efflux pump P-glycoprotein (P-gp) that would reduce its concentration within the vicinity of the cells and lead to the development of drug resistance. Hence, the incorporation of DCX into various nanocarrier systems has garnered a significant amount of attention in recent years to overcome these drawbacks. The surfaces of these drug-delivery systems indeed can be functionalized by modification with different ligands for smart targeting towards cancerous cells. This article provides an overview of the latest nanotechnological approaches and the delivery systems that were developed for passive and active delivery of DCX via different routes of administration for the treatment of lung cancer.
Keywords: docetaxel; drug delivery; lung cancer; nanoparticles; non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Denis J.N., Greene A.E., Guenard D., Gueritte-Voegelein F., Mangatal L., Potier P. Highly efficient, practical approach to natural taxol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988;110:5917–5919. doi: 10.1021/ja00225a063. - DOI
-
- Da Silva G.H., Fernandes M.A., Trevizan L.N.F., de Lima F.T., Eloy J.O., Chorilli M. A Critical Review of Properties and Analytical Methods for the Determination of Docetaxel in Biological and Pharmaceutical Matrices. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2018;48:517–527. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2018.1456315. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

