Aberrant Axo-Axonic Synaptic Reorganization in the Phosphorylated L1-CAM/Calcium Channel Subunit α2δ-1-Containing Central Terminals of Injured c-Fibers in the Spinal Cord of a Neuropathic Pain Model
- PMID: 33500315
- PMCID: PMC8174056
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0499-20.2021
Aberrant Axo-Axonic Synaptic Reorganization in the Phosphorylated L1-CAM/Calcium Channel Subunit α2δ-1-Containing Central Terminals of Injured c-Fibers in the Spinal Cord of a Neuropathic Pain Model
Abstract
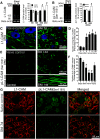
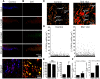
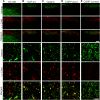
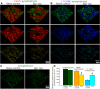
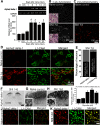
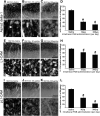
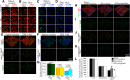
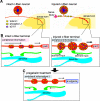
In the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, peripheral nerve injury induces structural and neurochemical alterations through which aberrant synaptic signals contribute to the formation of neuropathic pain. However, the role of injured primary afferent terminals in such plastic changes remain unclear. In this study, we investigated the effect of nerve injury on the morphology of cell adhesion molecule L1-CAM [total L1-CAM (tL1-CAM)]-positive primary afferent terminals and on the synaptic contact pattern in the dorsal horn. In the confocal images, the tL1-CAM-positive terminals showed morphologic changes leading to the formation of hypertrophic varicosities in the c-fiber terminal. These hypertrophic varicosities in the dorsal horn were co-labeled with phosphorylated (Ser1181) L1-CAM (pL1-CAM) and shown to store neurotransmitter peptides, but not when co-labeled with the presynaptic marker, synaptophysin. Quantitative analyses based on 3D-reconstructed confocal images revealed that peripheral nerve injury reduced dendritic synaptic contacts but promoted aberrant axo-axonic contacts on the tL1-CAM-positive hypertrophic varicosities. These tL1-CAM-positive varicosities co-expressed the injury-induced α2δ-1 subunit of the calcium channel in the dorsal horn. Administration of the anti-allodynic drug, pregabalin, inhibited accumulation of α2δ-1 and pL1-CAM associated with a reduction in hypertrophic changes of tL1-CAM-positive varicosities, and normalized injury-induced alterations in synaptic contacts in the dorsal horn. Our findings highlight the formation of aberrant spinal circuits that mediate the convergence of local neuronal signals onto injured c-fibers, suggesting that these hypertrophic varicosities may be important contributors to the pathologic mechanisms underlying neuropathic pain.
Keywords: axon terminal; cell adhesion; dorsal horn circuit; growth cone like structure; neuropathic pain; synaptic plasticity.
Copyright © 2021 Yamanaka et al.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Spinal dorsal horn calcium channel alpha2delta-1 subunit upregulation contributes to peripheral nerve injury-induced tactile allodynia.J Neurosci. 2004 Sep 29;24(39):8494-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2982-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15456823 Free PMC article.
-
Injury-specific functional alteration of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels in synaptic transmission of primary afferent C-fibers in the rat spinal superficial dorsal horn.Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Feb 5;772:11-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.12.031. Epub 2015 Dec 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26708163
-
Presynaptic NMDA receptors control nociceptive transmission at the spinal cord level in neuropathic pain.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 May;76(10):1889-1899. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03047-y. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30788514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alteration of the cell adhesion molecule L1 expression in a specific subset of primary afferent neurons contributes to neuropathic pain.Eur J Neurosci. 2007 Feb;25(4):1097-111. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05344.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17331206 Free PMC article.
-
α2δ-1-Linked NMDA and AMPA Receptors in Neuropathic Pain and Gabapentinoid Action.J Neurochem. 2025 Apr;169(4):e70064. doi: 10.1111/jnc.70064. J Neurochem. 2025. PMID: 40191897 Review.
Cited by
-
Analgesic effect of gastrin-releasing peptide in the dorsal horn.Mol Pain. 2022 Apr;18:17448069221108965. doi: 10.1177/17448069221108965. Mol Pain. 2022. PMID: 35815426 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA Receptors at Primary Afferent-Excitatory Neuron Synapses Differentially Sustain Chemotherapy- and Nerve Trauma-Induced Chronic Pain.J Neurosci. 2023 May 24;43(21):3933-3948. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0183-23.2023. Epub 2023 Apr 26. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37185237 Free PMC article.
-
Theta-Burst Stimulation of Primary Afferents Drives Long-Term Potentiation in the Spinal Cord and Persistent Pain via α2δ-1-Bound NMDA Receptors.J Neurosci. 2022 Jan 19;42(3):513-527. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1968-21.2021. Epub 2021 Dec 8. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34880118 Free PMC article.
-
Chicoric Acid Ameliorated Beta-Amyloid Pathology and Enhanced Expression of Synaptic-Function-Related Markers via L1CAM in Alzheimer's Disease Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 17;25(6):3408. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063408. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542381 Free PMC article.
-
The structure of sensory afferent compartments in health and disease.J Anat. 2022 Nov;241(5):1186-1210. doi: 10.1111/joa.13544. Epub 2021 Sep 15. J Anat. 2022. PMID: 34528255 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bauer CS, Nieto-Rostro M, Rahman W, Tran-Van-Minh A, Ferron L, Douglas L, Kadurin I, Sri Ranjan Y, Fernandez-Alacid L, Millar NS, Dickenson AH, Lujan R, Dolphin AC (2009) The increased trafficking of the calcium channel subunit alpha2delta-1 to presynaptic terminals in neuropathic pain is inhibited by the alpha2delta ligand pregabalin. J Neurosci 29:4076–4088. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0356-09.2009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cantí C, Nieto-Rostro M, Foucault I, Heblich F, Wratten J, Richards MW, Hendrich J, Douglas L, Page KM, Davies A, Dolphin AC (2005) The metal-ion-dependent adhesion site in the Von Willebrand factor-A domain of alpha2delta subunits is key to trafficking voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:11230–11235. 10.1073/pnas.0504183102 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
