Heat stress destabilizes symbiotic nutrient cycling in corals
- PMID: 33500354
- PMCID: PMC7865147
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2022653118
Heat stress destabilizes symbiotic nutrient cycling in corals
Abstract
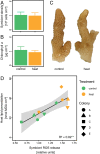
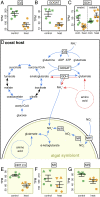
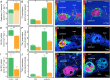
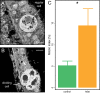
Recurrent mass bleaching events are pushing coral reefs worldwide to the brink of ecological collapse. While the symptoms and consequences of this breakdown of the coral-algal symbiosis have been extensively characterized, our understanding of the underlying causes remains incomplete. Here, we investigated the nutrient fluxes and the physiological as well as molecular responses of the widespread coral Stylophora pistillata to heat stress prior to the onset of bleaching to identify processes involved in the breakdown of the coral-algal symbiosis. We show that altered nutrient cycling during heat stress is a primary driver of the functional breakdown of the symbiosis. Heat stress increased the metabolic energy demand of the coral host, which was compensated by the catabolic degradation of amino acids. The resulting shift from net uptake to release of ammonium by the coral holobiont subsequently promoted the growth of algal symbionts and retention of photosynthates. Together, these processes form a feedback loop that will gradually lead to the decoupling of carbon translocation from the symbiont to the host. Energy limitation and altered symbiotic nutrient cycling are thus key factors in the early heat stress response, directly contributing to the breakdown of the coral-algal symbiosis. Interpreting the stability of the coral holobiont in light of its metabolic interactions provides a missing link in our understanding of the environmental drivers of bleaching and may ultimately help uncover fundamental processes underpinning the functioning of endosymbioses in general.
Keywords: coral bleaching; endosymbiosis; metabolic interaction; resource competition; selfish symbiont.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hoegh-Guldberg O., et al. , Coral reefs under rapid climate change and ocean acidification. Science 318, 1737–1742 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Hughes T. P., et al. , Global warming and recurrent mass bleaching of corals. Nature 543, 373–377 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Hughes T. P., et al. , Coral reefs in the Anthropocene. Nature 546, 82–90 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Rohwer F., Seguritan V., Azam F., Diversity and distribution of coral-associated bacteria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 243, 1–10 (2002).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

