Targeted delivery of extracellular vesicles in heart injury
- PMID: 33500724
- PMCID: PMC7797669
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.51571
Targeted delivery of extracellular vesicles in heart injury
Abstract
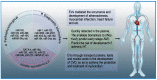
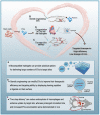
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nanoscale extracellular vesicles derived from endocytosis that are crucial to intercellular communication. EVs possess natural biocompatibility and stability that allow them to cross biological membranes and that protect them from degradation. Recent studies have shown that EVs-mediated crosstalk between different cell types in the heart could play important roles in the maintenance of cardiac homeostasis and the pathogenesis of heart diseases. In particular, EVs secreted by different types of stem cells exhibit cardioprotective effects. However, numerous studies have shown that intravenously injected EVs are quickly cleared by macrophages of the mononuclear phagocyte system (MPS) and preferentially accumulate in MPS organs such as the liver, spleen, and lung. In this review, we discuss exosome biogenesis, the role of EVs in heart diseases, and challenges in delivering EVs to the heart. Furthermore, we extensively discuss the targeted delivery of EVs for treating ischemic heart disease. These understandings will aid in the development of effective treatment strategies for heart diseases.
Keywords: Biogenesis; Challenges; Extracellular Vesicles; Heart Injury; Targeted Delivery.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- Hernesniemi JA, Lyytikainen LP, Oksala N, Seppala I, Kleber ME, Mononen N. et al. Predicting sudden cardiac death using common genetic risk variants for coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J. 2015;36:1669–75. - PubMed
-
- Al-Khatib SM, Stevenson WG, Ackerman MJ, Bryant WJ, Callans DJ, Curtis AB. et al. 2017 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for Management of Patients With Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72:e91–e220. - PubMed
-
- Higuchi A, Ku N-J, Tseng Y-C, Pan C-H, Li H-F, Kumar SS. et al. Stem cell therapies for myocardial infarction in clinical trials: bioengineering and biomaterial aspects. Lab Invest. 2017;97:1167–79. - PubMed
-
- Balbi C, Bollini S. Fetal and perinatal stem cells in cardiac regeneration: Moving forward to the paracrine era. Placenta. 2017;59:96–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

