Model Reference Predictive Adaptive Control for Large-Scale Soft Robots
- PMID: 33501321
- PMCID: PMC7806097
- DOI: 10.3389/frobt.2020.558027
Model Reference Predictive Adaptive Control for Large-Scale Soft Robots
Abstract
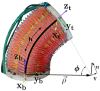
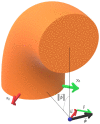
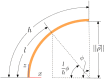
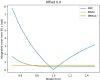
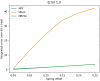
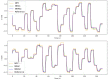
Past work has shown model predictive control (MPC) to be an effective strategy for controlling continuum joint soft robots using basic lumped-parameter models. However, the inaccuracies of these models often mean that an integral control scheme must be combined with MPC. In this paper we present a novel dynamic model formulation for continuum joint soft robots that is more accurate than previous models yet remains tractable for fast MPC. This model is based on a piecewise constant curvature (PCC) assumption and a relatively new kinematic representation that allows for computationally efficient state prediction. However, due to the difficulty in determining model parameters (e.g., inertias, damping, and spring effects) as well as effects common in continuum joint soft robots (hysteresis, complex pressure dynamics, etc.), we submit that regardless of the model selected, most model-based controllers of continuum joint soft robots would benefit from online model adaptation. Therefore, in this paper we also present a form of adaptive model predictive control based on model reference adaptive control (MRAC). We show that like MRAC, model reference predictive adaptive control (MRPAC) is able to compensate for "parameter mismatch" such as unknown inertia values. Our experiments also show that like MPC, MRPAC is robust to "structure mismatch" such as unmodeled disturbance forces not represented in the form of the adaptive regressor model. Experiments in simulation and hardware show that MRPAC outperforms individual MPC and MRAC.
Keywords: MRAC; adaptive control; continuum robot; dynamic modeling; model predictive control; parameter mismatch; soft robot; structure mismatch.
Copyright © 2020 Hyatt, Johnson and Killpack.
Figures



References
-
- Abdollahi A., Chowdhary G. (2019). Adaptive-optimal control under time-varying stochastic uncertainty using past learning. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 33, 1803–1824. 10.1002/acs.3061 - DOI
-
- Adetola V., DeHaan D., Guay M. (2009). Adaptive model predictive control for constrained nonlinear systems. Syst. Control Lett. 58, 320–326. 10.1016/j.sysconle.2008.12.002 - DOI
-
- Allen T. F., Rupert L., Duggan T. R., Hein G., Albert K. (2020). Closed-form non-singular constant-curvature continuum manipulator kinematics, in 2020 3rd IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (New Haven, CT: RoboSoft; ), 410–416. 10.1109/RoboSoft48309.2020.9116015 - DOI
-
- Best C. M., Gillespie M. T., Hyatt P., Rupert L., Sherrod V., Killpack M. D. (2016). A new soft robot control method: Using model predictive control for a pneumatically actuated humanoid. IEEE Robot. Autom. Magaz. 23, 75–84. 10.1109/MRA.2016.2580591 - DOI
-
- Bruno S., Sciavicco L., Villani L., Oriolo G. (2010). Robotics: Modelling, Planning and Control. London: Springer Science & Business Media.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

