Effective Multi-Mode Grasping Assistance Control of a Soft Hand Exoskeleton Using Force Myography
- PMID: 33501329
- PMCID: PMC7805723
- DOI: 10.3389/frobt.2020.567491
Effective Multi-Mode Grasping Assistance Control of a Soft Hand Exoskeleton Using Force Myography
Abstract
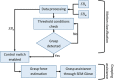
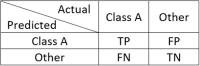
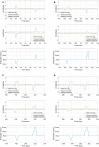
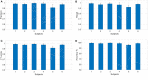
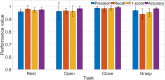
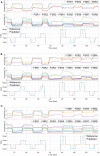
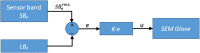
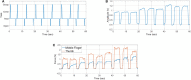
Human intention detection is fundamental to the control of robotic devices in order to assist humans according to their needs. This paper presents a novel approach for detecting hand motion intention, i.e., rest, open, close, and grasp, and grasping force estimation using force myography (FMG). The output is further used to control a soft hand exoskeleton called an SEM Glove. In this method, two sensor bands constructed using force sensing resistor (FSR) sensors are utilized to detect hand motion states and muscle activities. Upon placing both bands on an arm, the sensors can measure normal forces caused by muscle contraction/relaxation. Afterwards, the sensor data is processed, and hand motions are identified through a threshold-based classification method. The developed method has been tested on human subjects for object-grasping tasks. The results show that the developed method can detect hand motions accurately and to provide assistance w.r.t to the task requirement.
Keywords: FSR sensor band; exoskeleton control; grasping assistance; human intention detection; soft hand exoskeletons.
Copyright © 2020 Islam and Bai.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Design and Preliminary Feasibility Study of a Soft Robotic Glove for Hand Function Assistance in Stroke Survivors.Front Neurosci. 2017 Oct 9;11:547. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00547. eCollection 2017. Front Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29062267 Free PMC article.
-
Design and testing of fabric-based portable soft exoskeleton glove for hand grasping assistance in daily activity.HardwareX. 2024 May 7;18:e00537. doi: 10.1016/j.ohx.2024.e00537. eCollection 2024 Jun. HardwareX. 2024. PMID: 38784668 Free PMC article.
-
Flexo-glove: A 3D Printed Soft Exoskeleton Robotic Glove for Impaired Hand Rehabilitation and Assistance.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2018 Jul;2018:2120-2123. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2018.8512617. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2018. PMID: 30440822
-
A Review of Force Myography Research and Development.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Oct 20;19(20):4557. doi: 10.3390/s19204557. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31635167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moving toward Soft Robotics: A Decade Review of the Design of Hand Exoskeletons.Biomimetics (Basel). 2018 Jul 18;3(3):17. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics3030017. Biomimetics (Basel). 2018. PMID: 31105239 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of EMG-, FMG-, and EIT-Based Biosensors and Relevant Human-Machine Interactivities and Biomedical Applications.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 12;12(7):516. doi: 10.3390/bios12070516. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884319 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anam K., Rosyadi A. A., Sujanarko B., Al-Jumaily A. (2017). Myoelectric control systems for hand rehabilitation device: a review, in 2017 4th International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computer Science and Informatics (EECSI), 1–6. 10.1109/EECSI.2017.8239091 - DOI
-
- Arteaga M. V., Castiblanco J. C., Mondragon I. F., Colorado J. D., Alvarado-Rojas C. (2020). EMG-driven hand model based on the classification of individual finger movements. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 58:101834 10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101834 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

