Clinical significance of coronavirus disease 2019 in hospitalized patients with myocardial injury
- PMID: 33501708
- PMCID: PMC7943910
- DOI: 10.1002/clc.23530
Clinical significance of coronavirus disease 2019 in hospitalized patients with myocardial injury
Abstract
Background: The clinical significance of Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) as an associate of myocardial injury is controversial.
Hypothesis: Type 2 MI/Myocardial Injury are associated with worse outcomes if complicated by COVID-19.
Methods: This longitudinal cohort study involved consecutive patients admitted to a large urban hospital. Myocardial injury was determined using laboratory records as ≥1 hs-TnI result >99th percentile (male: >34 ng/L; female: >16 ng/L). Endotypes were defined according to the Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (MI) and COVID-19 determined using PCR. Outcomes of patients with myocardial injury with and without COVID-19 were assessed.
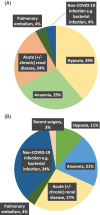
Results: Of 346 hospitalized patients with elevated hs-TnI, 35 (10.1%) had laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 (median age [IQR]; 65 [59-74]; 64.8% male vs. COVID-19 negative: 74 [63-83] years; 43.7% male). Cardiac endotypes by COVID-19 status (yes vs. no) were: Type 1 MI (0 [0%] vs. 115 [100%]; p < .0005), Type 2 MI (13 [16.5%] vs. 66 [83.5%]; p = .045), and non-ischemic myocardial injury (cardiac: 4 [5.8%] vs. 65 [94.2%]; p = .191, non-cardiac:19 [22.9%] vs. 64 [77.%]; p < .0005). COVID-19 patients had less comorbidity (median [IQR] Charlson Comorbidity Index: 3.0 [3.0] vs. 5.0 [4.0]; p = .001), similar hs-TnI concentrations (median [IQR] initial: 46 [113] vs. 62 [138]; p = .199, peak: 122 [474] vs. 79 [220] ng/L; p = .564), longer admission (days) (median [IQR]: 14[19] vs. 6[12]; p = .001) and higher in-hospital mortality (63.9% vs. 11.3%; OR = 13.2; 95%CI: 5.90, 29.7).
Conclusions: Cardiac sequelae of COVID-19 typically manifest as Non-cardiac myocardial injury/Type 2MI in younger patients with less co-morbidity. Paradoxically, the admission duration and in-hospital mortality are increased.
Keywords: COVID-19; Type 2 myocardial infarction; coronavirus; myocardial Injury; outcomes; troponin.
© 2020 The Authors. Clinical Cardiology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Colin Berry is employed by the University of Glasgow, which holds consultancy and research agreements with companies that have interests in the diagnosis and treatment of angina. The companies include Abbott Vascular, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Coroventis, GSK, HeartFlow, Medyria, Neovasc, Novartis and Siemens Healthcare.
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Clerkin KJ, Fried JA, Raikhelkar J, et al. COVID‐19 and cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2020;141:1648‐1655. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous