RPE-derived exosomes rescue the photoreceptors during retina degeneration: an intraocular approach to deliver exosomes into the subretinal space
- PMID: 33501868
- PMCID: PMC7850421
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2020.1870584
RPE-derived exosomes rescue the photoreceptors during retina degeneration: an intraocular approach to deliver exosomes into the subretinal space
Abstract
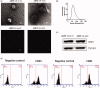
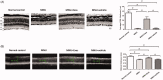
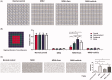
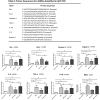
Retinal degeneration (RD) refers to a group of blinding retinopathies leading to the progressive photoreceptor demise and vision loss. Treatments against this debilitating disease are urgently needed. Intraocular delivery of exosomes represents an innovative therapeutic strategy against RD. In this study, we aimed to determine whether the subretinal delivery of RPE-derived exosomes (RPE-Exos) can prevent the photoreceptor death in RD. RD was induced in C57BL6 mice by MNU administration. These MNU administered mice received a single subretinal injection of RPE-Exos. Two weeks later, the RPE-Exos induced effects were evaluated via functional, morphological, and behavior examinations. Subretinal delivery of RPE-Exos efficiently ameliorates the visual function impairments, and alleviated the structural damages in the retina of MNU administered mice. Moreover, RPE-Exos exert beneficial effects on the electrical response of the inner retinal circuits. Treatment with RPE-Exos suppressed the expression levels of inflammatory factors, and mitigated the oxidative damage, indicating that subretinal delivery of RPE-Exos constructed a cytoprotective microenvironment in the retina of MNU administered mice. Our data suggest that RPE-Exos have therapeutic effects against the visual impairments and photoreceptor death. These findings will enrich our knowledge of RPE-Exos, and highlight the discovery of a promising medication for RD.
Keywords: Subretinal delivery; neural degeneration; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intravitreous Delivery of Αb-Crystallin Ameliorates N-Methyl-N-Nitrosourea Induced Photoreceptor Degeneration in Mice: An in vivo and ex vivo Study.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(5):2147-2160. doi: 10.1159/000492557. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30110696
-
Subcutaneous delivery of tauroursodeoxycholic acid rescues the cone photoreceptors in degenerative retina: A promising therapeutic molecule for retinopathy.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Sep;117:109021. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109021. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31387173
-
Therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on retinal detachment.Exp Eye Res. 2020 Feb;191:107899. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2019.107899. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Exp Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 31866431
-
What Can Pharmacological Models of Retinal Degeneration Tell Us?Curr Mol Med. 2017;17(2):100-107. doi: 10.2174/1566524017666170331162048. Curr Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28429669 Review.
-
Animal models for the evaluation of retinal stem cell therapies.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2025 May;106:101356. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2025.101356. Epub 2025 Apr 14. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2025. PMID: 40239758 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioprinting of exosomes: Prospects and challenges for clinical applications.Int J Bioprint. 2023 Feb 20;9(2):690. doi: 10.18063/ijb.690. eCollection 2023. Int J Bioprint. 2023. PMID: 37214319 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in engineered exosome-based therapies for ocular vascular disease.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jul 19;23(1):526. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03589-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40684186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Desmosome and Hemidesmosome Release via Exosomes from Retinal Pigmented Epithelium - A Precursor to Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Early AMD?Curr Eye Res. 2025 Mar 11:1-10. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2025.2469235. Online ahead of print. Curr Eye Res. 2025. PMID: 40070018 Review.
-
Emerging Role of Exosomes in Retinal Diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 1;9:643680. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.643680. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33869195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential in exosome-based targeted nano-drugs and delivery vehicles for posterior ocular disease treatment: from barriers to therapeutic application.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Jun;479(6):1319-1333. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04798-w. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37402019 Review.
References
-
- Ao J, Wood JP, Chidlow G, et al. (2018). Retinal pigment epithelium in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration and photobiomodulation as a potential therapy? Clin Exp Ophthalmol 46:670–86. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
