Bone Marrow and Peripheral Blood Findings in Patients Infected by SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33502434
- PMCID: PMC7929437
- DOI: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa274
Bone Marrow and Peripheral Blood Findings in Patients Infected by SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Objectives: Coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is associated with diverse clinical, including hematologic, abnormalities. We describe peripheral blood and bone marrow findings in deceased and living patients with COVID-19.
Methods: We examined bone marrows from 20 autopsies and 2 living patients with COVID-19 using H&E-stained slides and immunohistochemical stains. Clinical history and laboratory values were reviewed. HScore was calculated to estimate risk of hemophagocytic lymphohistocytosis (HLH).
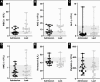
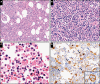
Results: The deceased patients included 12 men and 8 women (aged 32 to >89 years; median, 63 years). Hematologic abnormalities included frequent neutrophilic leukocytosis, lymphopenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia; one patient showed striking erythrocytosis. The bone marrows were all normocellular to hypercellular, most showing maturing trilineage hematopoiesis with myeloid left shift. In all 19 evaluable bone marrows, hemophagocytic histiocytes were identified. The HScore for secondary HLH ranged from 35 to 269 (median, 125; >169 in 5 patients). Coinfections were identified in 6 patients. In 2 living patients, bone marrow showed maturing trilineage hematopoiesis, including one showing few hemophagocytic histiocytes.
Conclusions: Peripheral blood from deceased patients with COVID-19 frequently showed neutrophilic leukocytosis, lymphopenia, and, rarely, secondary polycythemia; hemophagocytosis was common in their bone marrow. Consistent with other studies, we provide histopathologic evidence of secondary HLH development in patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: Bone marrow; CBC; COVID-19; Coronavirus; Hemophagocytosis; Peripheral blood; SARS-CoV-2.
© American Society for Clinical Pathology, 2021. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hemophagocytic histiocytosis in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: A bone marrow study.Int J Lab Hematol. 2021 Dec;43(6):1291-1301. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.13619. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Int J Lab Hematol. 2021. PMID: 34086418 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Infection-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis.Am J Clin Pathol. 2020 Sep 8;154(4):466-474. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa124. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32681166 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow haemophagocytosis indicates severe infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.Histopathology. 2021 Apr;78(5):727-737. doi: 10.1111/his.14281. Epub 2020 Dec 18. Histopathology. 2021. PMID: 33067892
-
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis diagnosed by bone marrow trephine biopsy in living post-COVID-19 patients: case report and mini-review.J Mol Histol. 2022 Aug;53(4):753-762. doi: 10.1007/s10735-022-10088-4. Epub 2022 Jun 14. J Mol Histol. 2022. PMID: 35699822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19-associated cytokine storm syndrome and diagnostic principles: an old and new Issue.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021 Dec;10(1):266-276. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1884503. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021. PMID: 33522893 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, a new cause of death during 'post-acute COVID-19 syndrome?' A case report.J Hematop. 2021 Apr 20;14(3):229-233. doi: 10.1007/s12308-021-00452-w. eCollection 2021 Sep. J Hematop. 2021. PMID: 33897909 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection augments species- and age-specific predispositions in cotton rats.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 14;13(1):757. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-27328-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36641520 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue by droplet digital PCR (ddPCR).Clin Chim Acta. 2022 Jul 1;532:181-187. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2022.05.007. Epub 2022 May 10. Clin Chim Acta. 2022. PMID: 35550815 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus dysregulates hematopoiesis and induces inflammaging of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.Exp Mol Med. 2025 Mar;57(3):616-627. doi: 10.1038/s12276-025-01416-1. Epub 2025 Mar 3. Exp Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40025168 Free PMC article.
-
Monocyte distribution width as a novel sepsis indicator in COVID-19 patients.BMC Infect Dis. 2022 Jan 4;22(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-07016-4. BMC Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 34983404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fan BE, Chong VCL, Chan SSW, et al. Hematologic parameters in patients with COVID-19 infection. Am J Hematol. 2020;95:E131-E134. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

