Meiotic chromosome axis remodelling is critical for meiotic recombination in Brassica rapa
- PMID: 33502451
- PMCID: PMC8023211
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erab035
Meiotic chromosome axis remodelling is critical for meiotic recombination in Brassica rapa
Abstract
Meiosis generates genetic variation through homologous recombination (HR) that is harnessed during breeding. HR occurs in the context of meiotic chromosome axes and the synaptonemal complex. To study the role of axis remodelling in crossover (CO) formation in a crop species, we characterized mutants of the axis-associated protein ASY1 and the axis-remodelling protein PCH2 in Brassica rapa. asy1 plants form meiotic chromosome axes that fail to synapse. CO formation is almost abolished, and residual chiasmata are proportionally enriched in terminal chromosome regions, particularly in the nucleolar organizing region (NOR)-carrying chromosome arm. pch2 plants show impaired ASY1 loading and remodelling, consequently achieving only partial synapsis, which leads to reduced CO formation and loss of the obligatory CO. PCH2-independent chiasmata are proportionally enriched towards distal chromosome regions. Similarly, in Arabidopsis pch2, COs are increased towards telomeric regions at the expense of (peri-) centromeric COs compared with the wild type. Taken together, in B. rapa, axis formation and remodelling are critical for meiotic fidelity including synapsis and CO formation, and in asy1 and pch2 CO distributions are altered. While asy1 plants are sterile, pch2 plants are semi-sterile and thus PCH2 could be an interesting target for breeding programmes.
Keywords: Brassica rapa; ASY1; PCH2; crossover; meiosis; meiotic chromosome axis remodelling; meiotic recombination; synaptonemal complex.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Figures

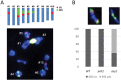
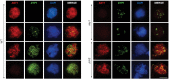
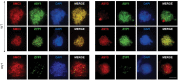

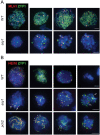

Comment in
-
Moving to and fro between Arabidopsis and its crop relatives confirms the role of chromosome remodelling on meiotic recombination.J Exp Bot. 2021 Apr 2;72(8):2811-2813. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erab032. J Exp Bot. 2021. PMID: 33822174 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
ZYP1-mediated recruitment of PCH2 to the synaptonemal complex remodels the chromosome axis leading to crossover restriction.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Dec 9;50(22):12924-12937. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1160. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36504011 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis PCH2 Mediates Meiotic Chromosome Remodeling and Maturation of Crossovers.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jul 16;11(7):e1005372. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005372. eCollection 2015 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26182244 Free PMC article.
-
ASYNAPSIS 1 ensures crossover fidelity in polyploid wheat by promoting homologous recombination and suppressing non-homologous recombination.Front Plant Sci. 2023 May 22;14:1188347. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1188347. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37284727 Free PMC article.
-
ASY1 coordinates early events in the plant meiotic recombination pathway.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2008;120(3-4):302-12. doi: 10.1159/000121079. Epub 2008 May 23. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2008. PMID: 18504359 Review.
-
Getting there: understanding the chromosomal recruitment of the AAA+ ATPase Pch2/TRIP13 during meiosis.Curr Genet. 2021 Aug;67(4):553-565. doi: 10.1007/s00294-021-01166-3. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33712914 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PCH-2 and meiotic HORMADs: A module for evolutionary innovation in meiosis?Curr Top Dev Biol. 2023;151:317-344. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2022.07.001. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36681475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromoanagenesis in the asy1 meiotic mutant of Arabidopsis.G3 (Bethesda). 2023 Feb 9;13(2):jkac185. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac185. G3 (Bethesda). 2023. PMID: 35920777 Free PMC article.
-
The proteome of developing barley anthers during meiotic prophase I.J Exp Bot. 2022 Mar 2;73(5):1464-1482. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erab494. J Exp Bot. 2022. PMID: 34758083 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic chromosome organization and its role in recombination and cancer.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2023;151:91-126. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2022.04.008. Epub 2022 Jun 20. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36681479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crossover interference mechanism: New lessons from plants.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 May 19;11:1156766. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1156766. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37274744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, et al. . 2003. Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301, 653–657. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong SJ, Caryl AP, Jones GH, Franklin FC. 2002. Asy1, a protein required for meiotic chromosome synapsis, localizes to axis-associated chromatin in Arabidopsis and Brassica. Journal of Cell Science 115, 3645–3655. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong SJ, Sanchez-Moran E, Franklin FCH. 2009. Cytological analysis of arabidopsis thaliana meiotic chromosomes. In: Keeney S, ed. Meiosis: volume 2, cytological methods. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press, 131–145. - PubMed
-
- Berchowitz LE, Copenhaver GP. 2008. Fluorescent Arabidopsis tetrads: a visual assay for quickly developing large crossover and crossover interference data sets. Nature Protocols 3, 41–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

