Aging and age-related diseases: from mechanisms to therapeutic strategies
- PMID: 33502634
- PMCID: PMC7838467
- DOI: 10.1007/s10522-021-09910-5
Aging and age-related diseases: from mechanisms to therapeutic strategies
Abstract
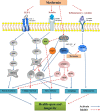
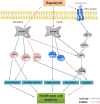
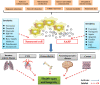
Aging is a physiological process mediated by numerous biological and genetic pathways, which are directly linked to lifespan and are a driving force for all age-related diseases. Human life expectancy has greatly increased in the past few decades, but this has not been accompanied by a similar increase in their healthspan. At present, research on aging biology has focused on elucidating the biochemical and genetic pathways that contribute to aging over time. Several aging mechanisms have been identified, primarily including genomic instability, telomere shortening, and cellular senescence. Aging is a driving factor of various age-related diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, immune system disorders, and musculoskeletal disorders. Efforts to find drugs that improve the healthspan by targeting the pathogenesis of aging have now become a hot topic in this field. In the present review, the status of aging research and the development of potential drugs for aging-related diseases, such as metformin, rapamycin, resveratrol, senolytics, as well as caloric restriction, are summarized. The feasibility, side effects, and future potential of these treatments are also discussed, which will provide a basis to develop novel anti-aging therapeutics for improving the healthspan and preventing aging-related diseases.
Keywords: Age‐related diseases; Aging; Anti‐aging drugs; Hallmarks of aging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

