Burkitt Lymphoma International Prognostic Index
- PMID: 33502927
- PMCID: PMC9851706
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.20.03288
Burkitt Lymphoma International Prognostic Index
Abstract
Purpose: Burkitt lymphoma (BL) has unique biology and clinical course but lacks a standardized prognostic model. We developed and validated a novel prognostic index specific for BL to aid risk stratification, interpretation of clinical trials, and targeted development of novel treatment approaches.
Methods: We derived the BL International Prognostic Index (BL-IPI) from a real-world data set of adult patients with BL treated with immunochemotherapy in the United States between 2009 and 2018, identifying candidate variables that showed the strongest prognostic association with progression-free survival (PFS). The index was validated in an external data set of patients treated in Europe, Canada, and Australia between 2004 and 2019.
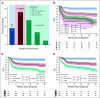
Results: In the derivation cohort of 633 patients with BL, age ≥ 40 years, performance status ≥ 2, serum lactate dehydrogenase > 3× upper limit of normal, and CNS involvement were selected as equally weighted factors with an independent prognostic value. The resulting BL-IPI identified groups with low (zero risk factors, 18% of patients), intermediate (one factor, 36% of patients), and high risk (≥ 2 factors, 46% of patients) with 3-year PFS estimates of 92%, 72%, and 53%, respectively, and 3-year overall survival estimates of 96%, 76%, and 59%, respectively. The index discriminated outcomes regardless of HIV status, stage, or first-line chemotherapy regimen. Patient characteristics, relative size of the BL-IPI groupings, and outcome discrimination were consistent in the validation cohort of 457 patients, with 3-year PFS estimates of 96%, 82%, and 63% for low-, intermediate-, and high-risk BL-IPI, respectively.
Conclusion: The BL-IPI provides robust discrimination of survival in adult BL, suitable for use as prognostication and stratification in trials. The high-risk group has suboptimal outcomes with standard therapy and should be considered for innovative treatment approaches.
Figures

References
-
- Molyneux EM, Rochford R, Griffin B, et al. : Burkitt's lymphoma. Lancet 379:1234-1244, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Jacobson C, LaCasce A: How I treat Burkitt lymphoma in adults. Blood 124:2913-2920, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Magrath I, Adde M, Shad A, et al. : Adults and children with small non-cleaved-cell lymphoma have a similar excellent outcome when treated with the same chemotherapy regimen. J Clin Oncol 14:925-934, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

