IS THE NEW PROCORE 20G DOUBLE FORWARD-BEVEL NEEDLE CAPABLE TO OBTAIN BETTER HISTOLOGICAL SAMPLES BY ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND FOR DIAGNOSING SOLID PANCREATIC LESIONS?
- PMID: 33503114
- PMCID: PMC7836075
- DOI: 10.1590/0102-672020200004e1554
IS THE NEW PROCORE 20G DOUBLE FORWARD-BEVEL NEEDLE CAPABLE TO OBTAIN BETTER HISTOLOGICAL SAMPLES BY ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND FOR DIAGNOSING SOLID PANCREATIC LESIONS?
Abstract
Background: Fine needle biopsy (FNB) histological samples by endoscopic ultrasound. It is important to obtain representative histological samples of solid biliopancreatic lesions without a clear indication for resection. The role of new needles in such task is yet to be determined.
Aim: To compare performance assessment between 20G double fine needle biopsy (FNB) and conventional 22G fine needle aspiration (FNA) needles for endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided biopsy.
Methods: This prospective study examined 20 patients who underwent the random puncture of solid pancreatic lesions with both needles and the analysis of tissue samples by a single pathologist.
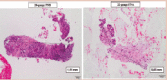
Results: The ProCore 20G FNB needle provided more adequate tissue samples (16 vs. 9, p=0.039) with better cellularity quantitative scores (11 vs. 5, p=0.002) and larger diameter of the histological sample (1.51±1.3 mm vs. 0.94±0.55 mm, p=0.032) than the 22G needle. The technical success, puncture difficulty, and sample bleeding were similar between groups. The sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy were 88.9%, 100%, and 90% and 77.8%, 100%, and 78.9% for the 20G and 22G needles, respectively.
Conclusions: The samples obtained with the ProCore 20G FNB showed better histological parameters; although there was no difference in the diagnostic performance between the two needles, these findings may improve pathologist performance.
Racional:: As lesões sólidas pancreáticas não ressecáveis cirurgicamente demandam boa amostragem tecidual para definição histológica e condução oncológica . O papel das novas agulhas de ecopunção no aprimoramento diagnóstico ainda necessita elucidação.
Objetivo:: Comparar as biópsias guiadas por ecoendoscoopia com a nova agulha 20G de bisel frontal duplo (FNB) com a agulha de aspiração fina 22G convencional.
Métodos:: Este estudo prospectivo avaliou 20 pacientes submetidos à punção de lesões pancreáticas sólidas com ambas agulhas e envolveu análise de amostras teciduais por um único patologista.
Resultados:: A agulha FNB 20G forneceu amostras de tecido mais adequadas (16 vs. 9, p=0,039) com melhores escores quantitativos de celularidade (11 vs. 5, p=0,002) e maior diâmetro máximo da amostra histológica (1,51±1,3 mm vs. 0,94±0,55 mm, p=0,032) que a agulha 22G. O sucesso técnico, dificuldade de punção e sangramento da amostra foram semelhantes entre os grupos. A sensibilidade, especificidade e acurácia diagnóstica foram 88,9%, 100% e 90% e 77,8%, 100% e 78,9% para as agulhas 20G e 22G, respectivamente.
Conclusão:: As amostras obtidas com a FNB 20G apresentaram melhores parâmetros histológicos, embora não tenha havido diferença no desempenho diagnóstico entre as duas agulhas.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Abdelgawwad MS, Alston E, Eltoum IA. The frequency and cancer risk associated with the atypical cytologic diagnostic category in endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration specimens of solid pancreatic lesions a meta-analysis and argument for a Bethesda System for Reporting Cytopathology of the Pancreas. Cancer Cytopathol. 2013;121:620–628. - PubMed
-
- Ardengh JC, Lopes CV, de Lima LFP. Cell block technique and cytological smears for the differential diagnosis of pancreatic neoplasms after endosonography-guided fine-needle aspiration. Acta Gastroenterol Latinoamericana. 2008;38:246–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical