Newborn mice form lasting CA2-dependent memories of their mothers
- PMID: 33503421
- PMCID: PMC7985754
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108668
Newborn mice form lasting CA2-dependent memories of their mothers
Abstract
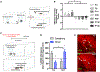
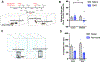
Some of the most enduring social connections begin when infants first recognize their caregivers, memories that form the basis of many family relationships. It remains unknown whether these early social memories persist into adulthood in mice and, if so, which brain regions support them. Here we show that mice form memories of their mother within days after birth and that these memories persist into adulthood. Pups display greater interest in the mother than in an unfamiliar dam before weaning, after which this preference reverses. Inhibition of CA2 neurons in the pup temporarily blocks the ability to discriminate between the mother and an unfamiliar dam, whereas doing so in adulthood prevents the formation of short-term memories about conspecifics, as well as social discrimination related to long-term memories of the mother. These results suggest that the CA2 supports memories of the mother during infancy and adulthood with a developmental switch in social preference.
Keywords: CA2; DREADDs; chemogenetic; development; hippocampus; immediate early gene; kin memory; mother memory; social investigation; social memory; social preference.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Postnatal development of hippocampal CA2 structure and function during the emergence of social recognition of peers.Hippocampus. 2023 Mar;33(3):208-222. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23476. Epub 2022 Oct 30. Hippocampus. 2023. PMID: 36309963 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphodiesterase 11A (PDE11A), Enriched in Ventral Hippocampus Neurons, is Required for Consolidation of Social but not Nonsocial Memories in Mice.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016 Nov;41(12):2920-2931. doi: 10.1038/npp.2016.106. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016. PMID: 27339393 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between infantile mother preference and neural regions activated by maternal contact in C57BL/6 mice.Neurosci Res. 2022 May;178:69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2022.01.008. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Neurosci Res. 2022. PMID: 35114216
-
Development of the hippocampal CA2 region and the emergence of social recognition.Dev Neurobiol. 2023 Jul-Sep;83(5-6):143-156. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22919. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Dev Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37326250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Ontogeny of Hippocampus-Dependent Memories.J Neurosci. 2021 Feb 3;41(5):920-926. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1651-20.2020. Epub 2020 Dec 16. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33328296 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Perineuronal net degradation rescues CA2 plasticity in a mouse model of Rett syndrome.J Clin Invest. 2021 Aug 16;131(16):e137221. doi: 10.1172/JCI137221. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 34228646 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of hippocampal area CA2 in hamster and vole brain.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 14:2024.02.12.579957. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.12.579957. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Comp Neurol. 2024 Mar;532(3):e25603. doi: 10.1002/cne.25603. PMID: 38405991 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Corticotropin-releasing hormone signaling from prefrontal cortex to lateral septum suppresses interaction with familiar mice.Cell. 2023 Sep 14;186(19):4152-4171.e31. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.08.010. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Cell. 2023. PMID: 37669667 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal exposure to the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist spironolactone disrupts hippocampal area CA2 connectivity and alters behavior in mice.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024 Dec;50(2):378-387. doi: 10.1038/s41386-024-01971-7. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39237618 Free PMC article.
-
RGS14 Regulation of Post-Synaptic Signaling and Spine Plasticity in Brain.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 25;22(13):6823. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136823. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34201943 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Armstrong CM, DeVito LM, and Cleland TA (2006). One-trial associative odor learning in neonatal mice. Chem. Senses 31, 343–349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

