Non-ionotropic NMDA receptor signaling gates bidirectional structural plasticity of dendritic spines
- PMID: 33503425
- PMCID: PMC7952241
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108664
Non-ionotropic NMDA receptor signaling gates bidirectional structural plasticity of dendritic spines
Abstract
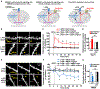
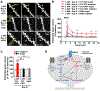
Experience-dependent refinement of neuronal connections is critically important for brain development and learning. Here, we show that ion-flow-independent NMDA receptor (NMDAR) signaling is required for the long-term dendritic spine growth that is a vital component of brain circuit plasticity. We find that inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK), which is downstream of non-ionotropic NMDAR signaling in long-term depression (LTD) and spine shrinkage, blocks long-term potentiation (LTP)-induced spine growth but not LTP. We hypothesize that non-ionotropic NMDAR signaling drives the cytoskeletal changes that support bidirectional spine structural plasticity. Indeed, we find that key signaling components downstream of non-ionotropic NMDAR function in LTD-induced spine shrinkage are also necessary for LTP-induced spine growth. Furthermore, NMDAR conformational signaling with coincident Ca2+ influx is sufficient to drive CaMKII-dependent long-term spine growth, even when Ca2+ is artificially driven through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Our results support a model in which non-ionotropic NMDAR signaling gates the bidirectional spine structural changes vital for brain plasticity.
Keywords: CaMKII; LTD; LTP; NMDA receptor; dendritic spine; non-ionotropic; p38 MAPK; structural plasticity.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson DR, Meyers MJ, Vernier WF, Mahoney MW, Kurumbail RG, Caspers N, Poda GI, Schindler JF, Reitz DB, and Mourey RJ (2007). Pyrrolopyridine inhibitors of mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 (MK-2). J. Med. Chem 50, 2647–2654. - PubMed
-
- Barria A, and Malinow R (2005). NMDA receptor subunit composition controls synaptic plasticity by regulating binding to CaMKII. Neuron 48, 289–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

