CDK2 limits the highly energetic secretory program of mature β cells by restricting PEP cycle-dependent KATP channel closure
- PMID: 33503433
- PMCID: PMC7882066
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108690
CDK2 limits the highly energetic secretory program of mature β cells by restricting PEP cycle-dependent KATP channel closure
Abstract
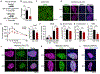
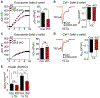
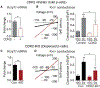
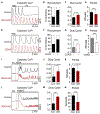
Hallmarks of mature β cells are restricted proliferation and a highly energetic secretory state. Paradoxically, cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) is synthesized throughout adulthood, its cytosolic localization raising the likelihood of cell cycle-independent functions. In the absence of any changes in β cell mass, maturity, or proliferation, genetic deletion of Cdk2 in adult β cells enhanced insulin secretion from isolated islets and improved glucose tolerance in vivo. At the single β cell level, CDK2 restricts insulin secretion by increasing KATP conductance, raising the set point for membrane depolarization in response to activation of the phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) cycle with mitochondrial fuels. In parallel with reduced β cell recruitment, CDK2 restricts oxidative glucose metabolism while promoting glucose-dependent amplification of insulin secretion. This study provides evidence of essential, non-canonical functions of CDK2 in the secretory pathways of quiescent β cells.
Keywords: CDK2; K(ATP) channel; PEP cycle; amplifying pathways; biosensor imaging; calcium; electrophysiology; insulin secretion; metabolic oscillations; β cell metabolism.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
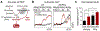
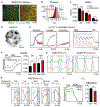
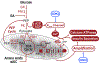
References
-
- Affourtit C, Alberts B, Barlow J, Carré JE, and Wynne AG (2018). Control of pancreatic β-cell bioenergetics. Biochem. Soc. Trans 46, 555–564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

