The Modern and Digital Transformation of Oral Health Care: A Mini Review
- PMID: 33503807
- PMCID: PMC7912705
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare9020118
The Modern and Digital Transformation of Oral Health Care: A Mini Review
Abstract
Dentistry is a part of the field of medicine which is advocated in this digital revolution. The increasing trend in dentistry digitalization has led to the advancement in computer-derived data processing and manufacturing. This progress has been exponentially supported by the Internet of medical things (IoMT), big data and analytical algorithm, internet and communication technologies (ICT) including digital social media, augmented and virtual reality (AR and VR), and artificial intelligence (AI). The interplay between these sophisticated digital aspects has dramatically changed the healthcare and biomedical sectors, especially for dentistry. This myriad of applications of technologies will not only be able to streamline oral health care, facilitate workflow, increase oral health at a fraction of the current conventional cost, relieve dentist and dental auxiliary staff from routine and laborious tasks, but also ignite participatory in personalized oral health care. This narrative article review highlights recent dentistry digitalization encompassing technological advancement, limitations, challenges, and conceptual theoretical modern approaches in oral health prevention and care, particularly in ensuring the quality, efficiency, and strategic dental care in the modern era of dentistry.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; augmented reality; big data; dental implants; digital dentistry; internet of things.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest in writing this article.
Figures

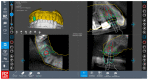
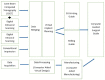
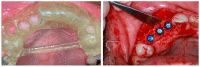
Similar articles
-
Recent Trends and Future Direction of Dental Research in the Digital Era.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Mar 18;17(6):1987. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17061987. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32197311 Free PMC article.
-
Disruptive Innovation in Dentistry: What It Is and What Could Be Next.J Dent Res. 2021 May;100(5):448-453. doi: 10.1177/0022034520978774. Epub 2020 Dec 16. J Dent Res. 2021. PMID: 33322997
-
Personalized workflows in reconstructive dentistry-current possibilities and future opportunities.Clin Oral Investig. 2022 Jun;26(6):4283-4290. doi: 10.1007/s00784-022-04475-0. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Clin Oral Investig. 2022. PMID: 35352184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gynecology Meets Big Data in the Disruptive Innovation Medical Era: State-of-Art and Future Prospects.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 May 11;18(10):5058. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18105058. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34064710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Assisted Biomedical Systems for Intelligent Healthcare.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 25;12(8):562. doi: 10.3390/bios12080562. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892459 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preliminary Novel Analysis on Antimicrobial Properties of Concentrated Growth Factor against Bacteria-Induced Oral Diseases.Eur J Dent. 2022 Oct;16(4):901-910. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1742121. Epub 2022 Feb 21. Eur J Dent. 2022. PMID: 35189641 Free PMC article.
-
A Contemporary Evaluation on Posterior Direct Restoration Teaching among Undergraduates in Dental Schools in Malaysia.Dent J (Basel). 2021 Oct 19;9(10):123. doi: 10.3390/dj9100123. Dent J (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34677185 Free PMC article.
-
The Association between Electronic Health Literacy and Oral Health Outcomes among Dental Patients in Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Study.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jun 20;11(12):1804. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11121804. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372921 Free PMC article.
-
Awareness and attitudes of primary healthcare physicians in cluster 2 toward healthcare transformation.J Family Med Prim Care. 2025 Jul;14(7):2653-2659. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_507_24. Epub 2025 Jul 21. J Family Med Prim Care. 2025. PMID: 40814535 Free PMC article.
-
Where Is the Artificial Intelligence Applied in Dentistry? Systematic Review and Literature Analysis.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Jul 8;10(7):1269. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10071269. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35885796 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

