Crystal Structure of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease in Complex with the Non-Covalent Inhibitor ML188
- PMID: 33503819
- PMCID: PMC7911568
- DOI: 10.3390/v13020174
Crystal Structure of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease in Complex with the Non-Covalent Inhibitor ML188
Abstract
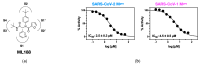
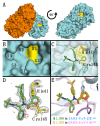
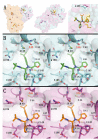
Viral proteases are critical enzymes for the maturation of many human pathogenic viruses and thus are key targets for direct acting antivirals (DAAs). The current viral pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 is in dire need of DAAs. The Main protease (Mpro) is the focus of extensive structure-based drug design efforts which are mostly covalent inhibitors targeting the catalytic cysteine. ML188 is a non-covalent inhibitor designed to target SARS-CoV-1 Mpro, and provides an initial scaffold for the creation of effective pan-coronavirus inhibitors. In the current study, we found that ML188 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Mpro at 2.5 µM, which is more potent than against SAR-CoV-1 Mpro. We determined the crystal structure of ML188 in complex with SARS-CoV-2 Mpro to 2.39 Å resolution. Sharing 96% sequence identity, structural comparison of the two complexes only shows subtle differences. Non-covalent protease inhibitors complement the design of covalent inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 main protease and are critical initial steps in the design of DAAs to treat CoVID 19.
Keywords: Covid-19; ML188; Mpro; SARS-CoV-2; crystal structure; direct-acting antivirals; main protease; protease inhibitor; structure-based drug design.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crystal structures of coronaviral main proteases in complex with the non-covalent inhibitor X77.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Sep;276(Pt 1):133706. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133706. Epub 2024 Jul 7. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38981557
-
In silico Study to Evaluate the Antiviral Activity of Novel Structures against 3C-like Protease of Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) and SARS-CoV.Med Chem. 2021;17(4):380-395. doi: 10.2174/1573396316999200727125522. Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32720605
-
SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors and activity-based probes for patient-sample imaging.Nat Chem Biol. 2021 Feb;17(2):222-228. doi: 10.1038/s41589-020-00689-z. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Nat Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 33093684
-
An Updated Review on SARS-CoV-2 Main Proteinase (MPro): Protein Structure and Small-Molecule Inhibitors.Curr Top Med Chem. 2021;21(6):442-460. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666201207095117. Curr Top Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33292134 Review.
-
Protease targeted COVID-19 drug discovery and its challenges: Insight into viral main protease (Mpro) and papain-like protease (PLpro) inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem. 2021 Jan 1;29:115860. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115860. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Bioorg Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33191083 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease (Mpro) as Anti-Coronavirus Agents.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 4;14(7):797. doi: 10.3390/biom14070797. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of the main protease of SARS-CoV-2 (Mpro) by repurposing/designing drug-like substances and utilizing nature's toolbox of bioactive compounds.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022;20:1306-1344. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.03.009. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35308802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protocetraric and Salazinic Acids as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 3CL Protease: Biochemical, Cytotoxic, and Computational Characterization of Depsidones as Slow-Binding Inactivators.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jun 4;15(6):714. doi: 10.3390/ph15060714. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35745633 Free PMC article.
-
Mpro-targeted anti-SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor-based drugs.J Chem Res. 2023 Jul 3;47(4):17475198231184799. doi: 10.1177/17475198231184799. eCollection 2023 Jul-Aug. J Chem Res. 2023. PMID: 37455837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro): Structure, function, and emerging therapies for COVID-19.MedComm (2020). 2022 Jul 14;3(3):e151. doi: 10.1002/mco2.151. eCollection 2022 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2022. PMID: 35845352 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Drosten C., Gunther S., Preiser W., van der Werf S., Brodt H.R., Becker S., Rabenau H., Panning M., Kolesnikova L., Fouchier R.A., et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1967–1976. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa030747. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

