Differences in Regulatory Mechanisms Induced by β-Lactoglobulin and κ-Casein in Cow's Milk Allergy Mouse Model-In Vivo and Ex Vivo Studies
- PMID: 33503831
- PMCID: PMC7911159
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13020349
Differences in Regulatory Mechanisms Induced by β-Lactoglobulin and κ-Casein in Cow's Milk Allergy Mouse Model-In Vivo and Ex Vivo Studies
Abstract
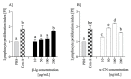
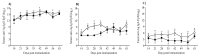
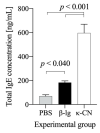
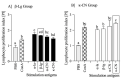
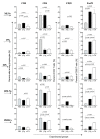
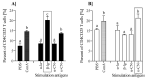
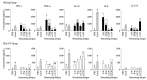
The presence of various proteins, including modified ones, in food which exhibit diverse immunogenic and sensitizing properties increases the difficulty of predicting host immune responses. Still, there is a lack of sufficiently reliable and comparable data and research models describing allergens in dietary matrices. The aim of the study was to estimate the immunomodulatory effects of β-lactoglobulin (β-lg) in comparison to those elicited by κ-casein (κ-CN), in vivo and ex vivo, using naïve splenocytes and a mouse sensitization model. Our results revealed that the humoral and cellular responses triggered by β-lg and κ-CN were of diverse magnitudes and showed different dynamics in the induction of control mechanisms. β-Lg turned out to be more immunogenic and induced a more dominant Th1 response than κ-CN, which triggered a significantly higher IgE response. For both proteins, CD4+ lymphocyte profiles correlated with CD4+CD25+ and CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T cells induction and interleukin 10 secretion, but β-lg induced more CD4+CD25+Foxp3- Tregs. Moreover, ex vivo studies showed the risk of interaction of immune responses to different milk proteins, which may exacerbate allergy, especially the one caused by β-lg. In conclusion, the applied model of in vivo and ex vivo exposure to β-lg and κ-CN showed significant differences in immunoreactivity of the tested proteins (κ-CN demonstrated stronger allergenic potential than β-lg), and may be useful for the estimation of allergenic potential of various food proteins, including those modified in technological processes.
Keywords: T cells; cow’s milk hypersensitivity; mouse model; β-lactoglobulin; κ-casein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Memory T cell proliferation in cow's milk allergy after CD25+ regulatory T cell removal suggests a role for casein-specific cellular immunity in IgE-mediated but not in non-IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2007;142(3):190-8. doi: 10.1159/000097021. Epub 2006 Nov 13. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17106206
-
B-cell epitopes as a screening instrument for persistent cow's milk allergy.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002 Aug;110(2):293-7. doi: 10.1067/mai.2002.126080. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12170271
-
Effect of Low-Immunogenic Yogurt Drinks and Probiotic Bacteria on Immunoreactivity of Cow's Milk Proteins and Tolerance Induction-In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Nutrients. 2020 Nov 4;12(11):3390. doi: 10.3390/nu12113390. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33158132 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed bacterial colonization of the gut alters the host immune response to oral sensitization against cow's milk proteins.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012 Dec;56(12):1838-47. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201200412. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2012. PMID: 23065810
-
[Sensitization to casein and beta-lactoglobulin (BLG) in children with cow's milk allergy (CMA)].Arerugi. 2010 Feb;59(2):117-22. Arerugi. 2010. PMID: 20212353 Japanese.
Cited by
-
Enhanced Effect of β-Lactoglobulin Immunization in Mice with Mild Intestinal Deterioration Caused by Low-Dose Dextran Sulphate Sodium: A New Experimental Approach to Allergy Studies.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 10;16(20):3430. doi: 10.3390/nu16203430. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39458426 Free PMC article.
-
The Immune System Response to 15-kDa Barley Protein: A Mouse Model Study.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 18;14(20):4371. doi: 10.3390/nu14204371. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36297055 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Study of Probiotics for Immunomodulation and Intervention in Food Allergy.Molecules. 2023 Jan 27;28(3):1242. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031242. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycation of Whey Proteins Increases the Ex Vivo Immune Response of Lymphocytes Sensitized to β-Lactoglobulin.Nutrients. 2023 Jul 12;15(14):3110. doi: 10.3390/nu15143110. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37513528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Foegeding E., Davis J.P., Doucet D., McGuffey M.K. Advances in modifying and understanding whey protein functionality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2002;13:151–159. doi: 10.1016/S0924-2244(02)00111-5. - DOI
-
- Wróblewska B., Juśkiewicz J., Kroplewski B., Jurgoński A., Wasilewska E., Złotkowska D., Markiewicz L. The effects of whey and soy proteins on growth performance, gastrointestinal digestion, and selected physiological responses in rats. Food Funct. 2018;9:1500–1509. doi: 10.1039/C7FO01204G. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

