Antiviral Activity of Jamaican Medicinal Plants and Isolated Bioactive Compounds
- PMID: 33503834
- PMCID: PMC7865499
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26030607
Antiviral Activity of Jamaican Medicinal Plants and Isolated Bioactive Compounds
Abstract
Plants have had historical significance in medicine since the beginning of civilization. The oldest medical pharmacopeias of the African, Arabian, and Asian countries solely utilize plants and herbs to treat pain, oral diseases, skin diseases, microbial infections, multiple types of cancers, reproductive disorders among a myriad of other ailments. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that over 65% of the world population solely utilize botanical preparations as medicine. Due to the abundance of plants, plant-derived medicines are more readily accessible, affordable, convenient, and have safer side-effect profiles than synthetic drugs. Plant-based decoctions have been a significant part of Jamaican traditional folklore medicine. Jamaica is of particular interest because it has approximately 52% of the established medicinal plants that exist on earth. This makes the island particularly welcoming for rigorous scientific research on the medicinal value of plants and the development of phytomedicine thereof. Viral infections caused by the human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 (HIV-1 and HIV-2), hepatitis virus B and C, influenza A virus, and the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS CoV-2) present a significant global burden. This is a review of some important Jamaican medicinal plants, with particular reference to their antiviral activity.
Keywords: antivirals; phytoantiviral; phytomedicine; viral infections.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors H.L. and N.T. are employees of Vilotos and Flavocure and both companies have commercial interest in Caflanone. The other authors declare no conflict of interest. Neither Vilotos nor Flavocure took part in the study or experience.
Figures

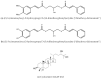
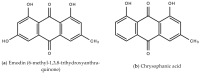
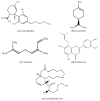
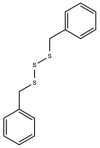
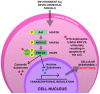
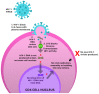
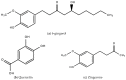

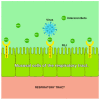
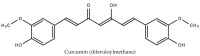
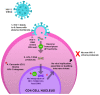
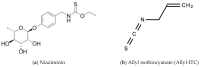
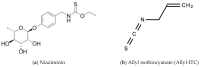




References
-
- Robinson M.M., Zhang X. The World Medicines Situation 2011: Traditional Medicines: Global Situation, Issues and Challenges. 3rd ed. World Health Organization (WHO); Geneva, Switzerland: 2011.
-
- Barnes J., Anderson L.A., Phillipson J.D. Herbal medicines: A Guide for Health-Care Professionals. 3rd ed. Pharmaceutical Press; London, UK: 2007.
-
- Krishnaiah D., Sarbatly R., Nithyanandam R. A review of the antioxidant potential of medicinal plant species. Food Bioprod. Process. 2011;89:217–233. doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2010.04.008. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

