Efficacy of Providing the PI3K p110α Inhibitor BYL719 (Alpelisib) to Middle-Aged Mice in Their Diet
- PMID: 33503847
- PMCID: PMC7911305
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11020150
Efficacy of Providing the PI3K p110α Inhibitor BYL719 (Alpelisib) to Middle-Aged Mice in Their Diet
Abstract
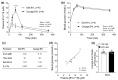
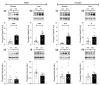
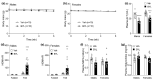
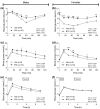
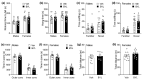
BYL719 (alpelisib) is a small molecule inhibitor of PI3K p110α developed for cancer therapy. Targeted suppression of PI3K has led to lifespan extension in rodents and model organisms. If PI3K inhibitors are to be considered as an aging therapeutic, it is important to understand the potential consequences of long-term exposure, and the most practical way to achieve this is through diet administration. Here, we investigated the pharmacokinetics of BYL719 delivered in diet and the efficacy of BYL719 to suppress insulin signaling when administered in the diet of 8-month-old male and female mice. Compared to oral gavage, diet incorporation resulted in a lower peak plasma BYL719 (3.6 vs. 9.2 μM) concentration but similar half-life (~1.5 h). Consuming BYL719 resulted in decreased insulin signaling in liver and muscle within 72 h, and mice still showed impaired glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity following 6 weeks of access to a diet containing 0.3 g/kg BYL719. However, consuming BYL719 did not affect food intake, body mass, muscle function (rotarod and hang time performance) or cognitive behaviors. This provides evidence that BYL719 has long-term efficacy without major toxicity or side effects, and suggests that administering BYL719 in diet is suitable for studying the effect of pharmacological suppression of PI3K p110α on aging and metabolic function.
Keywords: BYL-719; aging; glucose tolerance; insulin signaling; pharmacokinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prolonged treatment with a PI3K p110α inhibitor causes sex- and tissue-dependent changes in antioxidant content, but does not affect mitochondrial function.Biosci Rep. 2020 Oct 30;40(10):BSR20201128. doi: 10.1042/BSR20201128. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33006363 Free PMC article.
-
Specific inhibition of p110α subunit of PI3K: putative therapeutic strategy for KRAS mutant colorectal cancers.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 18;7(42):68546-68558. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11843. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27602501 Free PMC article.
-
Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of [(14)C]BYL719 (alpelisib) in healthy male volunteers.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015 Oct;76(4):751-60. doi: 10.1007/s00280-015-2842-4. Epub 2015 Aug 8. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26254025
-
Alpelisib to treat breast cancer.Drugs Today (Barc). 2020 Jun;56(6):357-363. doi: 10.1358/dot.2020.56.6.3137526. Drugs Today (Barc). 2020. PMID: 32525134 Review.
-
Treatment of diabetes with vanadium salts: general overview and amelioration of nutritionally induced diabetes in the Psammomys obesus gerbil.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2001 Jan-Feb;17(1):55-66. doi: 10.1002/1520-7560(2000)9999:9999<::aid-dmrr165>3.0.co;2-j. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2001. PMID: 11241892 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Hormonal Therapy in Breast Cancer and Its Effect on the Blood-Brain Barrier.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 19;14(20):5132. doi: 10.3390/cancers14205132. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chaperone-mediated autophagy as a modulator of aging and longevity.Front Aging. 2024 Dec 2;5:1509400. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2024.1509400. eCollection 2024. Front Aging. 2024. PMID: 39687864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual inhibition of EGFR and PI3Kinase signaling in EGFR amplified triple negative breast cancer cells induces apoptosis and reduces tumor growth.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 7:2025.06.03.657674. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.03.657674. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40501689 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
PI3K inhibitors are finally coming of age.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021 Oct;20(10):741-769. doi: 10.1038/s41573-021-00209-1. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 34127844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary supplementation of clinically utilized PI3K p110α inhibitor extends the lifespan of male and female mice.Nat Aging. 2023 Feb;3(2):162-172. doi: 10.1038/s43587-022-00349-y. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Nat Aging. 2023. PMID: 37118113
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

