Summary of Natural Products Ameliorate Concanavalin A-Induced Liver Injury: Structures, Sources, Pharmacological Effects, and Mechanisms of Action
- PMID: 33503905
- PMCID: PMC7910830
- DOI: 10.3390/plants10020228
Summary of Natural Products Ameliorate Concanavalin A-Induced Liver Injury: Structures, Sources, Pharmacological Effects, and Mechanisms of Action
Abstract
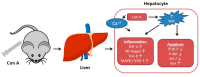
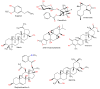
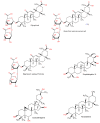
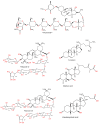
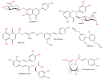
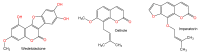
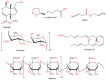
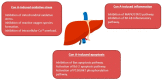
Liver diseases represent a threat to human health and are a significant cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide. Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a progressive and chronic hepatic inflammatory disease, which may lead to severe complications. Concanavalin A (Con A)-induced hepatic injury is regarded as an appropriate experimental model for investigating the pathology and mechanisms involved in liver injury mediated by immune cells as well as T cell-related liver disease. Despite the advances in modern medicine, the only available strategies to treat AIH, include the use of steroids either solely or with immunosuppressant drugs. Unfortunately, this currently available treatment is associated with significant side-effects. Therefore, there is an urgent need for safe and effective drugs to replace and/or supplement those in current use. Natural products have been utilized for treating liver disorders and have become a promising therapy for various liver disorders. In this review, the natural compounds and herbal formulations as well as extracts and/or fractions with protection against liver injury caused by Con A and the underlying possible mechanism(s) of action are reviewed. A total of 53 compounds from different structural classes are discussed and over 97 references are cited. The goal of this review is to attract the interest of pharmacologists, natural product researchers, and synthetic chemists for discovering novel drug candidates for treating immune-mediated liver injury.
Keywords: autoimmune hepatitis; concanavalin A; drug discovery; inflammation; liver diseases; mechanism of action; natural products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Concanavalin-A as a Model for Induction of Murine Autoimmune Hepatitis: Role of TNF-α and NF-κβ During The Acute Phase.Egypt J Immunol. 2020 Jun;27(2):19-30. Egypt J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33548974
-
Toll-like receptor 5 signaling restrains T-cell/natural killer T-cell activation and protects against concanavalin A-induced hepatic injury.Hepatology. 2017 Jun;65(6):2059-2073. doi: 10.1002/hep.29140. Epub 2017 May 4. Hepatology. 2017. PMID: 28273362
-
The farnesyltransferase inhibitor tipifarnib protects against autoimmune hepatitis induced by Concanavalin A.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Jun;83:106462. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106462. Epub 2020 Apr 3. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32251961
-
Concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis model in mice: Mechanisms and future outlook.Open Life Sci. 2022 Feb 28;17(1):91-101. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0013. eCollection 2022. Open Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35291566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental hepatitis and role of cytokines.Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 1997 Apr-Jun;60(2):176-9. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 1997. PMID: 9260332 Review.
Cited by
-
Alpha-Mangostin as a New Therapeutic Candidate for Concanavalin A-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis: Impact on the SIRT1/Nrf2 and NF-κB Crosstalk.Plants (Basel). 2022 Sep 19;11(18):2441. doi: 10.3390/plants11182441. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145841 Free PMC article.
-
Kaempferol sophoroside glucoside mitigates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity: Role of Nrf2/NF-κB and JNK/ASK-1 signaling pathways.Heliyon. 2024 May 17;10(10):e31448. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31448. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38813141 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review of Tripterygium wilfordii hook. f. in the treatment of rheumatic and autoimmune diseases: Bioactive compounds, mechanisms of action, and future directions.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 1;14:1282610. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1282610. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38027004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effect of Ginsenoside CK against Autoimmune Hepatitis Induced by Concanavalin A.Foods. 2023 Dec 5;12(24):4379. doi: 10.3390/foods12244379. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38137182 Free PMC article.
-
The Combination of Tradition and Future: Data-Driven Natural-Product-Based Treatments for Parkinson's Disease.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Jul 14;2021:9990020. doi: 10.1155/2021/9990020. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34335855 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gantner F., Leist M., Lohse A.W., Germann P.G., Tiegs G. Concanavalin A-induced T-cell-mediated hepatic injury in mice: The role of tumor necrosis factor. Hepatology. 1995;21:190–198. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

