Additive Manufacturing of Oral Tablets: Technologies, Materials and Printed Tablets
- PMID: 33504009
- PMCID: PMC7912000
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13020156
Additive Manufacturing of Oral Tablets: Technologies, Materials and Printed Tablets
Abstract
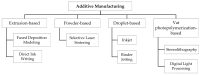
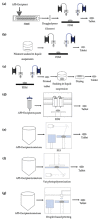
Additive manufacturing (AM), also known as three-dimensional (3D) printing, enables fabrication of custom-designed and personalized 3D constructs with high complexity in shape and composition. AM has a strong potential to fabricate oral tablets with enhanced customization and complexity as compared to tablets manufactured using conventional approaches. Despite these advantages, AM has not yet become the mainstream manufacturing approach for fabrication of oral solid dosage forms mainly due to limitations of AM technologies and lack of diverse printable drug formulations. In this review, AM of oral tablets are summarized with respect to AM technology. A detailed review of AM methods and materials used for the AM of oral tablets is presented. This article also reviews the challenges in AM of pharmaceutical formulations and potential strategies to overcome these challenges.
Keywords: 3D printing; drug delivery; hydrogel; pharmaceutical; polymer; precision medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
3D printing of tablets using inkjet with UV photoinitiation.Int J Pharm. 2017 Aug 30;529(1-2):523-530. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.06.085. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Int J Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28673860
-
3D Printing of Solid Oral Dosage Forms: Numerous Challenges With Unique Opportunities.J Pharm Sci. 2020 Dec;109(12):3535-3550. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2020.08.029. Epub 2020 Sep 23. J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 32976900 Review.
-
3D printed oral solid dosage form: Modified release and improved solubility.J Control Release. 2022 Nov;351:407-431. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.09.023. Epub 2022 Sep 27. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 36122897 Review.
-
Emergence of 3D Printed Dosage Forms: Opportunities and Challenges.Pharm Res. 2016 Aug;33(8):1817-32. doi: 10.1007/s11095-016-1933-1. Epub 2016 May 18. Pharm Res. 2016. PMID: 27194002 Review.
-
3D-Printed Oral Dosage Forms: Mechanical Properties, Computational Approaches and Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Sep 3;13(9):1401. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091401. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575475 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Behavior of Aqueous Medicated Inks on Porous Tablet Surfaces.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jul 14;17(7):908. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070908. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40733116 Free PMC article.
-
A Bibliometric Analysis of 3D Printing in Personalized Medicine Research from 2012 to 2022.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 26;16(11):1521. doi: 10.3390/ph16111521. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Additive Manufacturing MicroFactory: Overcoming Brittle Material Failure and Improving Product Performance through Tablet Micro-Structure Control for an Immediate Release Dose Form.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Sep 11;16(18):2566. doi: 10.3390/polym16182566. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39339030 Free PMC article.
-
Review: Continuous Manufacturing of Small Molecule Solid Oral Dosage Forms.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Aug 22;13(8):1311. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081311. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34452272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coupling of Fused Deposition Modeling and Inkjet Printing to Produce Drug Loaded 3D Printed Tablets.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jan 10;14(1):159. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14010159. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35057054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bharawaj S., Jain V., Sharma S., Jat R.C., Jain S. Orally Disintegrating Tablets: A Review. Drug Invent. Today. 2010;2:81–88.
-
- Panigrahi R., Behera S.P., Panda C.S. A Review on Fast Dissolving Tablets. WebmedCentral Pharm. Sci. 2010;1:7–17.
-
- Pawar P.B., Mansuk A., Ramteke K., Sharma Y., Patil S. Mouth dissolving tablet: A review. Int. J. Herb. Drug Res. 2011;1:22–29.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

