Circulating microRNA Panel as a Potential Novel Biomarker for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Diagnosis
- PMID: 33504017
- PMCID: PMC7865311
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13030449
Circulating microRNA Panel as a Potential Novel Biomarker for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Diagnosis
Abstract
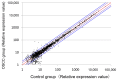
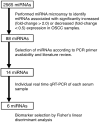
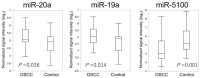
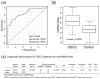
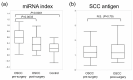
A lack of reliable biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) poses a major clinical issue. The sensitivity and specificity of classical serum tumor markers, such as the squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCC-Ag), are quite poor, especially for early detection. This study aimed to identify specific serum miRNAs potentially serving as OSCC biomarkers. The expression levels of candidate miRNAs in serum samples from 40 OSCC patients and 40 healthy controls were quantitatively analyzed via microarray and reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) analyses. To enhance the accuracy of detection, we used Fisher's linear discriminant analysis to establish a diagnostic model that incorporated a combination of selected miRNAs. Consequently, miR-19a and miR-20a were significantly upregulated in the patient group (p = 0.014 and 0.036, respectively), whereas miR-5100 was downregulated (p = 0.001). We found that a combination of six miRNAs (miR-24, miR-20a, miR-122, miR-150, miR-4419a, and miR-5100) could distinguish between OSCC and the control group with a higher degree of accuracy (Area Under the Curve, AUC: 0.844, sensitivity: 55%, and specificity: 92.5%). Furthermore, compared to serum SCC antigen, the 6-miRNA panel could accurately detect the presence of OSCC. The present specific miRNAs panel may serve as a novel candidate biomarker of oral cancer.
Keywords: biomarker; microRNA; oral cancer; oral squamous cell carcinoma; tumor marker.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The clinical implications of circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers in screening oral squamous cell carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 17;12:965357. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.965357. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36465364 Free PMC article.
-
Serum miR-483-5p: a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jan;37(1):447-53. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3514-z. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26224475
-
A panel of six-circulating miRNA signature in serum and its potential diagnostic value in colorectal cancer.Life Sci. 2020 Oct 1;258:118226. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118226. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32771555
-
Salivary exosomal miR-24-3p serves as a potential detective biomarker for oral squamous cell carcinoma screening.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Jan;121:109553. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109553. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31704611
-
Circulating miR-21 as a Potential Biomarker for the Diagnosis of Oral Cancer: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 10;12(4):936. doi: 10.3390/cancers12040936. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32290144 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long Non-Coding LEF1-AS1 Sponge miR-5100 Regulates Apoptosis and Autophagy in Gastric Cancer Cells via the miR-5100/DEK/AMPK-mTOR Axis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 26;23(9):4787. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094787. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563178 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating miRNA as a Biomarker in Oral Cancer Liquid Biopsy.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 21;11(3):965. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030965. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Predictive Value of BUB1 in the Prognosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int Dent J. 2025 Apr;75(2):1165-1175. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2024.07.012. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Int Dent J. 2025. PMID: 39147662 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical implications of circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers in screening oral squamous cell carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 17;12:965357. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.965357. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36465364 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Neck Lymph Node Metastasis-Specific microRNA-Implication for Use in Monitoring or Prediction of Neck Lymph Node Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jul 25;15(15):3769. doi: 10.3390/cancers15153769. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang S.F., Wei F.C., Liao C.T., Wang H.M., Lin C.Y., Lo S., Huang J.J., Chen I.H., Kang C.J., Chien H.T., et al. Risk stratification in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma by preoperative CRP and SCC antigen levels. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012;19:3856–3864. doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2392-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roman E., Lunde M.L., Miron T., Warnakulasauriya S., Johannessen A.C., Vasstrand E.N., Ibrahim S.O. Analysis of protein expression profile of oral squamous cell carcinoma by MALDI-TOF-MS. Anticancer Res. 2013;33:837–845. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

