Optimization of Chitosan Glutaraldehyde-Crosslinked Beads for Reactive Blue 4 Anionic Dye Removal Using a Surface Response Methodology
- PMID: 33504022
- PMCID: PMC7912159
- DOI: 10.3390/life11020085
Optimization of Chitosan Glutaraldehyde-Crosslinked Beads for Reactive Blue 4 Anionic Dye Removal Using a Surface Response Methodology
Abstract
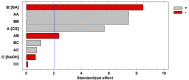
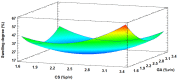
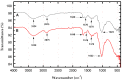
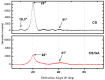
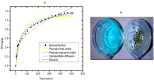
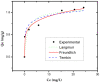
The use of dyes at an industrial level has become problematic, since the discharge of dye effluents into water disturbs the photosynthetic activity of numerous aquatic organisms by reducing the penetration of light and oxygen, in addition to causing carcinogenic diseases and mutagenic effects in humans, as well as alterations in different ecosystems. Chitosan (CS) is suitable for removing anionic dyes since it has favorable properties, such as acquiring a positive charge and a typical macromolecular structure of polysaccharides. In this study, the optimization of CS beads crosslinked with glutaraldehyde (GA) for the adsorption of reactive blue dye 4 (RB4) in an aqueous solution was carried out. In this sense, the response surface methodology (RSM) was applied to evaluate the concentration of CS, GA, and sodium hydroxide on the swelling degree in the GA-crosslinked CS beads. In the same way, RSM was applied to optimize the adsorption process of the RB4 dye as a function of the initial pH of the solution, initial concentration of the dye, and adsorbent dose. The crosslinking reaction was investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and X-ray diffractometry (XRD). The design described for the swelling degree showed an R2 (coefficient of determination) adjusted of 0.8634 and optimized concentrations (CS 3.3% w/v, GA 1.7% v/v, and NaOH 1.3 M) that were conveniently applied with a concentration of CS at 3.0% w/v to decrease the viscosity and facilitate the formation of the beads. In the RB4 dye adsorption design, an adjusted R2 (0.8280) with good correlation was observed, where the optimized conditions were: pH = 2, adsorbent dose 0.6 g, and initial concentration of RB4 dye 5 mg/L. The kinetic behavior and the adsorption isotherm allowed us to conclude that the GA-crosslinked CS beads' adsorption mechanism was controlled mainly by chemisorption interactions, demonstrating its applicability in systems that require the removal of contaminants with similar structures to the model presented.
Keywords: adsorption; crosslinking chitosan beads; experimental design; glutaraldehyde; reactive blue 4 dye; removal efficiency; swelling degree.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Alver E., Metin A.Ü. Anionic dye removal from aqueous solutions using modified zeolite: Adsorption kinetics and isotherm studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2012;200:59–67. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.06.038. - DOI
-
- Greluk M., Hubicki Z. Efficient removal of Acid Orange 7 dye from water using the strongly basic anion exchange resin Amberlite IRA-958. Desalination. 2011;278:219–226. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2011.05.024. - DOI
-
- Chowdhury S., Mishra R., Saha P., Kushwaha P. Adsorption thermodynamics, kinetics and isosteric heat of adsorption of malachite green onto chemically modified rice husk. Desalination. 2011;265:159–168. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2010.07.047. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

