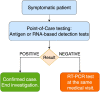
Urgent need for evaluation of point-of-care tests as an RT-PCR-sparing strategy for the diagnosis of Covid-19 in symptomatic patients
- PMID: 33504404
- PMCID: PMC7870902
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268821000170
Urgent need for evaluation of point-of-care tests as an RT-PCR-sparing strategy for the diagnosis of Covid-19 in symptomatic patients
Keywords: COVID-19; pandemic; public health emerging infections.
Conflict of interest statement
I declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Response to Letter to Editor by Zavascki A.P.: Urgent need for evaluating point-of-care tests as a RT-PCR-sparing strategy for the diagnosis of Covid-19 in symptomatic patients.Epidemiol Infect. 2021 Jan 28;149:e33. doi: 10.1017/S0950268821000182. Epidemiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 33504396 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Comment on
-
A discussion on implementing pooling detection tests of novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) for a large population.Epidemiol Infect. 2021 Jan 5;149:e17. doi: 10.1017/S0950268820003155. Epidemiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 33397529 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Response to Letter to Editor by Zavascki A.P.: Urgent need for evaluating point-of-care tests as a RT-PCR-sparing strategy for the diagnosis of Covid-19 in symptomatic patients.Epidemiol Infect. 2021 Jan 28;149:e33. doi: 10.1017/S0950268821000182. Epidemiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 33504396 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Multi-center evaluation of cepheid xpert® xpress SARS-CoV-2 point-of-care test during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.J Clin Virol. 2020 Jul;128:104426. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104426. Epub 2020 May 11. J Clin Virol. 2020. PMID: 32417674 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of performance of two SARS-CoV-2 Rapid IgM-IgG combined antibody tests on capillary whole blood samples from the fingertip.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 17;15(9):e0237694. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237694. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32941461 Free PMC article.
-
[SARS-CoV-2 and Microbiological Diagnostic Dynamics in COVID-19 Pandemic].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2020 Jul;54(3):497-509. doi: 10.5578/mb.69839. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2020. PMID: 32755524 Review. Turkish.
-
Thoracic imaging tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 30;9:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 26;11:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub3. PMID: 32997361 Updated.
Cited by
-
Response to Letter to Editor by Zavascki A.P.: Urgent need for evaluating point-of-care tests as a RT-PCR-sparing strategy for the diagnosis of Covid-19 in symptomatic patients.Epidemiol Infect. 2021 Jan 28;149:e33. doi: 10.1017/S0950268821000182. Epidemiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 33504396 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comparative Analysis of RT-PCR and a Colloidal Gold Immunochromatographic Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Detection.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 May 28;15(11):1362. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15111362. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40506934 Free PMC article.
-
A discussion on the minimum required number of tests in two common pooling test methods for SARS-CoV-2.Epidemiol Infect. 2021 Aug 3;149:e179. doi: 10.1017/S0950268821001667. Epidemiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 34340721 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howson ELA et al. (2021) Preliminary optimisation of a simplified sample preparation method to permit direct detection of SARS-CoV-2 within saliva samples using reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP). Journal of Virological Methods 289, 114048. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2020.114048. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical