Altered high-density lipoprotein composition and functions during severe COVID-19
- PMID: 33504824
- PMCID: PMC7841145
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-81638-1
Altered high-density lipoprotein composition and functions during severe COVID-19
Abstract
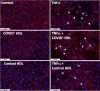
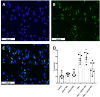
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is affecting millions of patients worldwide. The consequences of initial exposure to SARS-CoV-2 go beyond pulmonary damage, with a particular impact on lipid metabolism. Decreased levels in HDL-C were reported in COVID-19 patients. Since HDL particles display antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and potential anti-infectious properties, we aimed at characterizing HDL proteome and functionality during COVID-19 relative to healthy subjects. HDLs were isolated from plasma of 8 severe COVID-19 patients sampled at admission to intensive care unit (Day 1, D1) at D3 and D7, and from 16 sex- and age-matched healthy subjects. Proteomic analysis was performed by LC-MS/MS. The relative amounts of proteins identified in HDLs were compared between COVID-19 and controls. apolipoprotein A-I and paraoxonase 1 were confirmed by Western-blot analysis to be less abundant in COVID-19 versus controls, whereas serum amyloid A and alpha-1 antitrypsin were higher. HDLs from patients were less protective in endothelial cells stiumalted by TNFα (permeability, VE-cadherin disorganization and apoptosis). In these conditions, HDL inhibition of apoptosis was blunted in COVID-19 relative to controls. In conclusion, we show major changes in HDL proteome and decreased functionality in severe COVID-19 patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
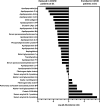
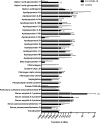
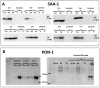
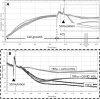
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

