Effects of tilt on cerebral hemodynamics measured by NeoDoppler in healthy neonates
- PMID: 33504967
- PMCID: PMC8566239
- DOI: 10.1038/s41390-020-01354-w
Effects of tilt on cerebral hemodynamics measured by NeoDoppler in healthy neonates
Abstract
Background: Today, there are conflicting descriptions of how neonates respond to tilt. Examining physiologic responses of cerebral blood flow velocities (BFVs) in challenging situations like a tilt requires equipment that can cope with positional changes. We aimed to characterize how healthy term neonates respond to mild cerebral hemodynamic stress induced by a 90° tilt test using the recently developed NeoDoppler ultrasound system.
Methods: A small ultrasound probe was fixated to the neonatal fontanel by a cap, and measured cerebral BFV in healthy neonates during and after a 90° head-up tilt test, five min in total, at their first and second day of life. Unsupervised k-means cluster analysis was used to characterize common responses.
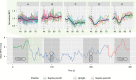
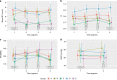
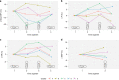
Results: Fifty-six ultrasound recordings from 36 healthy term neonates were analyzed. We identified five distinct, immediate responses that were related to specific outcomes in BFV, heart rate, and pulsatility index the next two min. Among 20 neonates with two recordings, 13 presented with different responses in the two tests.
Conclusions: Instant changes in cerebral BFV were detected during the head-up tilt tests, and the cluster analysis identified five different hemodynamic responses. Continuous recordings revealed that the differences between groups persisted two min after tilt.
Impact: NeoDoppler is a pulsed-wave Doppler ultrasound system with a probe fixated to the neonatal fontanel by a cap that can measure continuous cerebral blood flow velocity. Healthy neonates present with a range of normal immediate cerebral hemodynamic responses to a 90° head-up tilt, categorized in five groups by cluster analysis. This paper adds new knowledge about connection between immediate responses and prolonged responses to tilt. We demonstrate that the NeoDoppler ultrasound system can detect minute changes in cerebral blood flow velocity during a 90° head-up tilt.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: NTNU and St. Olavs hospital, Trondheim University Hospital may benefit financially from a commercialization of the ultrasound equipment through future possible intellectual properties; this may include financial benefits to authors of this article. H.T. and S.A.N. are co‐inventors of NeoDoppler and have part-time positions in CIMON Medical, the company that is responsible for commercialization of NeoDoppler. H.T. and S.A.N. are among the shareholders in CIMON Medical. S.S.Ø. and A.H.J. declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

