Computational approach for the identification of putative allergens from Cucurbitaceae family members
- PMID: 33505071
- PMCID: PMC7813966
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-020-04539-7
Computational approach for the identification of putative allergens from Cucurbitaceae family members
Abstract
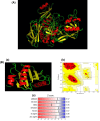
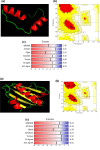
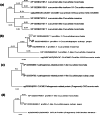
Certain substances referred to as allergens, induce hypersensitivity (allergic reactions) which normally are considered to be innocuous, are small in size and incite IgE response. This study was focused to predict the putative allergens from other Cucurbitaceae family members using computational approach by analyzing the already reported allergens of the same family. The four reported allergens Cuc m 1, Cuc m 2, Cuc m 3 and Citr I 2 of Cucurbitaceae family were obtained from International Union of Immunological Societies, in which three were from Cucumis melo (Muskmelon) and one from Citrullus lanatus (Watermelon) respectively. BlastP analysis reported 44 similar sequences to these allergens from other members of Cucurbitaceae family namely Cucurbita moschata, Cucurbita pepo and Cucurbita maxima. The allergenicity of these sequences was predicted using AlgPred tool in which it revealed 26 protein sequences as putative allergens. These selected sequences were further analyzed for their physicochemical properties using ProtParam tool in which 13 sequences were found to satisfy the required parameters, and therefore further analyzed by AllerMatch™ and AllergenOnline tools to check the Codex Alimentarius rules for allergens. Finally, 13 sequences that were selected were structurally analyzed for similarity using PROMALS3D tool and phylogenetic relationship was established with the reported allergens using MEGA-X software. It was concluded that 13 sequences from Cucurbitaceae family belonging to different species of Pumpkin showed potential allergenicity based on the computational analysis that possibly can play a role in allergies and cross reactivity.
Keywords: Allergenicity prediction; Allergens; Cucurbitaceae; Phylogenetic analysis; Structural proteomics.
© Association of Food Scientists & Technologists (India) 2020.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
