Proteomic evaluation of kimchi, a traditional Korean fermented vegetable, and comparison of kimchi manufactured in China and Korea
- PMID: 33505084
- PMCID: PMC7813951
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-020-04777-9
Proteomic evaluation of kimchi, a traditional Korean fermented vegetable, and comparison of kimchi manufactured in China and Korea
Abstract
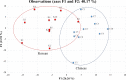
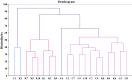
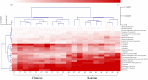
Kimchi is a traditional Korean fermented vegetable, which is also widely consumed in Japan and China. However, little is known about the kimchi proteome. In this study, Korean and Chinese kimchi proteomes were evaluated by shotgun proteomics. A total of 250 proteins were annotated, and 29 of these were expressed at > 1% of the average relative abundance. Discrimination of the geographical origins of Korean and Chinese kimchi samples was possible using multivariate analysis of the proteomic data, and 23 proteins were expressed differently between the two types (p < 0.001), and represent possible markers to discriminate between Chinese and Korean kimchi. This study provides important insights into the kimchi proteome and illustrates the proteomic differences caused by geographical origin.
Keywords: Geographical origin; Kimchi; Proteomic analysis; Shotgun proteomics.
© Association of Food Scientists & Technologists (India) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ananey-Obiri D, Matthews L, Azahrani MH, Ibrahim SA, Galanakis CM, Tahergorabi R. Application of protein-based edible coatings for fat uptake reduction in deep-fat fried foods with an emphasis on muscle food proteins. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2018;80:167–174. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2018.08.012. - DOI
-
- Barba FJ, Galanakis CM, Esteve MJ, Frigola A, Vorobiev E. Potential use of pulsed electric technologies and ultrasounds to improve the recovery of high-added value compounds from blackberries. J Food Eng. 2015;167:38–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2015.02.001. - DOI
-
- Bursac Kovacevic D, Barba FJ, Granato D, Galanakis CM, Herceg Z, Dragovic-Uzelac V, Putnik P. Pressurized hot water extraction (PHWE) for the green recovery of bioactive compounds and steviol glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni leaves. Food Chem. 2018;254:150–157. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.01.192. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
