Three-dimensional multicellular cell culture for anti-melanoma drug screening: focus on tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 33505112
- PMCID: PMC7817757
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-020-00440-5
Three-dimensional multicellular cell culture for anti-melanoma drug screening: focus on tumor microenvironment
Abstract
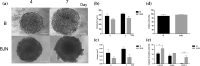
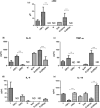
Abstract: The development of new treatments for malignant melanoma, which has the worst prognosis among skin neoplasms, remains a challenge. The tumor microenvironment aids tumor cells to grow and resist to chemotherapeutic treatment. One way to mimic and study the tumor microenvironment is by using three-dimensional (3D) co-culture models (spheroids). In this study, a melanoma heterospheroid model composed of cancer cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages was produced by liquid-overlay technique using the agarose gel. The size, growth, viability, morphology, cancer stem-like cells population and inflammatory profile of tumor heterospheroids and monospheroids were analyzed to evaluate the influence of stromal cells on these parameters. Furthermore, dacarbazine cytotoxicity was evaluated using spheroids and two-dimensional (2D) melanoma model. After finishing the experiments, it was observed the M2 macrophages induced an anti-inflammatory microenvironment in heterospheroids; fibroblasts cells support the formation of the extracellular matrix, and a higher percentage of melanoma CD271 was observed in this model. Additionally, melanoma spheroids responded differently to the dacarbazine than the 2D melanoma culture as a result of their cellular heterogeneity and 3D structure. The 3D model was shown to be a fast and reliable tool for drug screening, which can mimic the in vivo tumor microenvironment regarding interactions and complexity.
Keywords: 3D cell culture; Co-culture; Melanoma; Tumor microenvironment; Tumor spheroid.
© Springer Nature B.V. 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- American Cancer Society (2019) Chemotherapy for Melanoma Skin Cancer. Available at https://www.cancer.org/cancer/melanoma-skin-cancer/treating/chemotherapy.... Accessed 6 Jun 2020
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

