Stimulating the Resolution of Inflammation Through Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in COVID-19: Rationale for the COVID-Omega-F Trial
- PMID: 33505321
- PMCID: PMC7830247
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2020.624657
Stimulating the Resolution of Inflammation Through Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in COVID-19: Rationale for the COVID-Omega-F Trial
Abstract
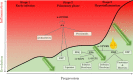
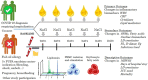
Infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). SARS-CoV-2 triggers an immune response with local inflammation in the lung, which may extend to a systemic hyperinflammatory reaction. Excessive inflammation has been reported in severe cases with respiratory failure and cardiovascular complications. In addition to the release of cytokines, referred to as cytokine release syndrome or "cytokine storm," increased pro-inflammatory lipid mediators derived from the omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) arachidonic acid may cause an "eicosanoid storm," which contributes to the uncontrolled systemic inflammation. Specialized pro-resolving mediators, which are derived from omega-3 PUFA, limit inflammatory reactions by an active process called resolution of inflammation. Here, the rationale for omega-3 PUFA supplementation in COVID-19 patients is presented along with a brief overview of the study protocol for the trial "Resolving Inflammatory Storm in COVID-19 Patients by Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids - A single-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled feasibility study" (COVID-Omega-F). EudraCT: 2020-002293-28; clinicaltrials.gov: NCT04647604.
Keywords: COVID-19; clinical trial; eicosanoids; omega-3 fatty acids; resolution of inflammation.
Copyright © 2021 Arnardottir, Pawelzik, Öhlund Wistbacka, Artiach, Hofmann, Reinholdsson, Braunschweig, Tornvall, Religa and Bäck.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

