Comparative Genomics of Leuconostoc carnosum
- PMID: 33505375
- PMCID: PMC7829361
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.605127
Comparative Genomics of Leuconostoc carnosum
Abstract
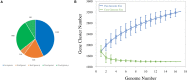
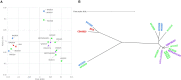
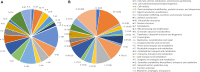
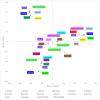
Leuconostoc carnosum is a known colonizer of meat-related food matrices. It reaches remarkably high loads during the shelf life in packaged meat products and plays a role in spoilage, although preservative effects have been proposed for some strains. In this study, the draft genomes of 17 strains of L. carnosum (i.e., all the strains that have been sequenced so far) were compared to decipher their metabolic and functional potential and to determine their role in food transformations. Genome comparison and pathway reconstruction indicated that L. carnosum is a compact group of closely related heterofermentative bacteria sharing most of the metabolic features. Adaptation to a nitrogen-rich environment, such as meat, is evidenced by 23 peptidase genes identified in the core genome and by the autotrophy for nitrogen compounds including several amino acids, vitamins, and cofactors. Genes encoding the decarboxylases yielding biogenic amines were not present. All the strains harbored 1-4 of 32 different plasmids, bearing functions associated to proteins hydrolysis, transport of amino acids and oligopeptides, exopolysaccharides, and various resistances (e.g., to environmental stresses, bacteriophages, and heavy metals). Functions associated to bacteriocin synthesis, secretion, and immunity were also found in plasmids. While genes for lactococcin were found in most plasmids, only three harbored the genes for leucocin B, a class IIa antilisterial bacteriocin. Determinants of antibiotic resistances were absent in both plasmids and chromosomes.
Keywords: Leuconostoc carnosum; bacteriocin; genomics; metabolism; pangenome analysis.
Copyright © 2021 Candeliere, Raimondi, Spampinato, Tay, Amaretti, Schlundt and Rossi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Budde B. B., Hornbaek T., Jacobsen T., Barkholt V., Koch A. G. (2003). Leuconostoc carnosum 4010 has the potential for use as a protective culture for vacuum-packed meats: culture isolation, bacteriocin identification, and meat application experiments. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 83 171–184. 10.1016/S0168-1605(02)00364-1 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

